Protective Role of Rabbit Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain-2 (NOD2)-Mediated Signaling Pathway in Resistance to Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Infection
- PMID: 29998088
- PMCID: PMC6031198
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00220
Protective Role of Rabbit Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain-2 (NOD2)-Mediated Signaling Pathway in Resistance to Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Infection
Abstract
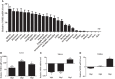
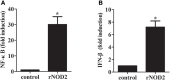
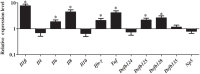
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2 (NOD2), a member of the NOD-like receptors (NLRs) family that is well-known to play a key role in innate immune responses and is involved in innate antibacterial responses. In this study, rabbit NOD2 (rNOD2) was cloned from rabbit kidney (RK) cells. It was distributed in various tissues, and the highest level of rNod2 was detected in spleen. Moreover, the expression of rNod2 was significantly upregulated in the heart, liver, and spleen induced by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC). Overexpression of rNOD2 induced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine, including Il1β, Il6, Ifn-γ, and Tnf, as well as defensins, including Defb124, Defb125, and Defb128 through the nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling pathway. Furthermore, overexpression of rNOD2 inhibited the growth of EHEC, and knockdown of rNOD2 or inhibition of the NF-κB pathway promoted its replication. In addition, our results suggest that rNOD2 can significantly activate NF-κB signaling and trigger antibacterial defenses to increase the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and defensins after stimulation by EHEC. These findings are useful to further understanding the innate immune system of rabbits and providing a new perspective for the prevention of bacterial diseases in rabbits.
Keywords: EHEC; NF-κB; NOD2; antibacterial ability; rabbits.
Figures



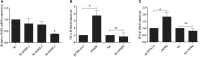


Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of NLRX1 in rabbit during enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli infection.Dev Comp Immunol. 2020 May;106:103612. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103612. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Dev Comp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31962226
-
Characterization of Rabbit Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain 1 (NOD1) and the Role of NOD1 Signaling Pathway during Bacterial Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Oct 10;8:1278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01278. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29067026 Free PMC article.
-
Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli serogroup O111 inhibits NF-(kappa)B-dependent innate responses in a manner independent of a type III secreted OspG orthologue.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Oct;155(Pt 10):3214-3225. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.030759-0. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19628559
-
Nod1 and Nod2 in innate immunity and human inflammatory disorders.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Dec;35(Pt 6):1479-84. doi: 10.1042/BST0351479. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 18031249 Review.
-
The Inflammatory Response during Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Aug;2(4):EHEC-0012-2013. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.EHEC-0012-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104206 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Role of Inflammation and Metabolites in Bell's Palsy and Potential Treatment Strategies.Biomedicines. 2025 Apr 13;13(4):957. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040957. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang M., Wang T., Nie P., Zou J., Secombes C. J. (2011). Cloning of two rainbow trout nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 (NOD2) splice variants and functional characterization of the NOD2 effector domains. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 30, 118–127. 10.1016/j.fsi.2010.09.014 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

