Effect of Acupuncture vs Sham Acupuncture or Waitlist Control on Joint Pain Related to Aromatase Inhibitors Among Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 29998338
- PMCID: PMC6583520
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.8907
Effect of Acupuncture vs Sham Acupuncture or Waitlist Control on Joint Pain Related to Aromatase Inhibitors Among Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Musculoskeletal symptoms are the most common adverse effects of aromatase inhibitors and often result in therapy discontinuation. Small studies suggest that acupuncture may decrease aromatase inhibitor-related joint symptoms.
Objective: To determine the effect of acupuncture in reducing aromatase inhibitor-related joint pain.
Design, setting, and patients: Randomized clinical trial conducted at 11 academic centers and clinical sites in the United States from March 2012 to February 2017 (final date of follow-up, September 5, 2017). Eligible patients were postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer who were taking an aromatase inhibitor and scored at least 3 on the Brief Pain Inventory Worst Pain (BPI-WP) item (score range, 0-10; higher scores indicate greater pain).
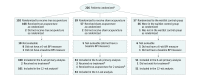
Interventions: Patients were randomized 2:1:1 to the true acupuncture (n = 110), sham acupuncture (n = 59), or waitlist control (n = 57) group. True acupuncture and sham acupuncture protocols consisted of 12 acupuncture sessions over 6 weeks (2 sessions per week), followed by 1 session per week for 6 weeks. The waitlist control group did not receive any intervention. All participants were offered 10 acupuncture sessions to be used between weeks 24 and 52.
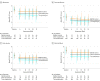
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was the 6-week BPI-WP score. Mean 6-week BPI-WP scores were compared by study group using linear regression, adjusted for baseline pain and stratification factors (clinically meaningful difference specified as 2 points).
Results: Among 226 randomized patients (mean [SD] age, 60.7 [8.6] years; 88% white; mean [SD] baseline BPI-WP score, 6.6 [1.5]), 206 (91.1%) completed the trial. From baseline to 6 weeks, the mean observed BPI-WP score decreased by 2.05 points (reduced pain) in the true acupuncture group, by 1.07 points in the sham acupuncture group, and by 0.99 points in the waitlist control group. The adjusted difference for true acupuncture vs sham acupuncture was 0.92 points (95% CI, 0.20-1.65; P = .01) and for true acupuncture vs waitlist control was 0.96 points (95% CI, 0.24-1.67; P = .01). Patients in the true acupuncture group experienced more grade 1 bruising compared with patients in the sham acupuncture group (47% vs 25%; P = .01).
Conclusions and relevance: Among postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer and aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgias, true acupuncture compared with sham acupuncture or with waitlist control resulted in a statistically significant reduction in joint pain at 6 weeks, although the observed improvement was of uncertain clinical importance.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01535066.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Acupuncture for Aromatase Inhibitor-Related Joint Pain Among Breast Cancer Patients.JAMA. 2018 Dec 4;320(21):2269-2270. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.16736. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 30512092 No abstract available.
-
Acupuncture for Aromatase Inhibitor-Related Joint Pain Among Breast Cancer Patients.JAMA. 2018 Dec 4;320(21):2270. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.16740. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 30512093 No abstract available.
References
-
- Burstein HJ, Lacchetti C, Anderson H, et al. . Adjuvant endocrine therapy for women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update on Ovarian Suppression. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(14):1689-1701. - PubMed
-
- Crew KD, Greenlee H, Capodice J, et al. . Prevalence of joint symptoms in postmenopausal women taking aromatase inhibitors for early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(25):3877-3883. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

