Alzheimer's Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Is Rapidly Seeded by Herpesviridae to Protect against Brain Infection
- PMID: 30001512
- PMCID: PMC6075814
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.06.030
Alzheimer's Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Is Rapidly Seeded by Herpesviridae to Protect against Brain Infection
Erratum in
-
Alzheimer's Disease-Associated β-Amyloid Is Rapidly Seeded by Herpesviridae to Protect against Brain Infection.Neuron. 2018 Dec 19;100(6):1527-1532. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.043. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30571943 No abstract available.
Abstract
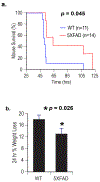
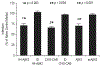
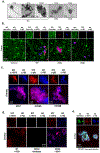
Amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) fibrilization and deposition as β-amyloid are hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. We recently reported Aβ is an innate immune protein that protects against fungal and bacterial infections. Fibrilization pathways mediate Aβ antimicrobial activities. Thus, infection can seed and dramatically accelerate β-amyloid deposition. Here, we show Aβ oligomers bind herpesvirus surface glycoproteins, accelerating β-amyloid deposition and leading to protective viral entrapment activity in 5XFAD mouse and 3D human neural cell culture infection models against neurotropic herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV1) and human herpesvirus 6A and B. Herpesviridae are linked to AD, but it has been unclear how viruses may induce β-amyloidosis in brain. These data support the notion that Aβ might play a protective role in CNS innate immunity, and suggest an AD etiological mechanism in which herpesviridae infection may directly promote Aβ amyloidosis.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-β; antimicrobial peptide; herpes simplex virus 1; herpesviridae; herpesvirus glycoprotein; human herpesvirus 6; infection; oligomers; β-amyloid peptide.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
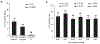
Comment in
-
Microbes and Alzheimer's Disease: New Findings Call for a Paradigm Change.Trends Neurosci. 2018 Sep;41(9):570-573. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Trends Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30033181
References
-
- Alonso R, Pisa D, Marina AI, Morato E, Rabano A, and Carrasco L (2014). Fungal infection in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 41, 301–311. - PubMed
-
- Arnusch CJ, Branderhorst H, de Kruijff B, Liskamp RMJ, Breukink E, and Pieters RJ (2007). Enhanced membrane pore formation by multimeric/oligomeric antimicrobial peptides. Biochemistry 46, 13437–13442. - PubMed
-
- Bourgade K, Garneau H, Giroux G, Le Page AY, Bocti C, Dupuis G, Frost EH, and Fulop T Jr. (2015). β-Amyloid peptides display protective activity against the human Alzheimer’s disease-associated herpes simplex virus-1. Biogerontology 16, 85–98. - PubMed
-
- Bourgade K, Le Page A, Bocti C, Witkowski JM, Dupuis G, Frost EH, and Fulop T (2016). Protective Effect of Amyloid-β Peptides Against Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Infection in a Neuronal Cell Culture Model. J Alzheimers Dis 50, 1227–1241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

