Myocardial Scar and Mortality in Severe Aortic Stenosis
- PMID: 30002099
- PMCID: PMC6221382
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032839
Myocardial Scar and Mortality in Severe Aortic Stenosis
Abstract
Background: Aortic valve replacement (AVR) for aortic stenosis is timed primarily on the development of symptoms, but late surgery can result in irreversible myocardial dysfunction and additional risk. The aim of this study was to determine whether the presence of focal myocardial scar preoperatively was associated with long-term mortality.
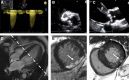
Methods: In a longitudinal observational outcome study, survival analysis was performed in patients with severe aortic stenosis listed for valve intervention at 6 UK cardiothoracic centers. Patients underwent preprocedural echocardiography (for valve severity assessment) and cardiovascular magnetic resonance for ventricular volumes, function and scar quantification between January 2003 and May 2015. Myocardial scar was categorized into 3 patterns (none, infarct, or noninfarct patterns) and quantified with the full width at half-maximum method as percentage of the left ventricle. All-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality were tracked for a minimum of 2 years.
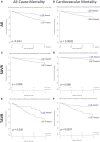
Results: Six hundred seventy-four patients with severe aortic stenosis (age, 75±14 years; 63% male; aortic valve area, 0.38±0.14 cm2/m2; mean gradient, 46±18 mm Hg; left ventricular ejection fraction, 61.0±16.7%) were included. Scar was present in 51% (18% infarct pattern, 33% noninfarct). Management was surgical AVR (n=399) or transcatheter AVR (n=275). During follow-up (median, 3.6 years), 145 patients (21.5%) died (52 after surgical AVR, 93 after transcatheter AVR). In multivariable analysis, the factors independently associated with all-cause mortality were age (hazard ratio [HR], 1.50; 95% CI, 1.11-2.04; P=0.009, scaled by epochs of 10 years), Society of Thoracic Surgeons score (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22; P=0.007), and scar presence (HR, 2.39; 95% CI, 1.40-4.05; P=0.001). Scar independently predicted all-cause (26.4% versus 12.9%; P<0.001) and cardiovascular (15.0% versus 4.8%; P<0.001) mortality, regardless of intervention (transcatheter AVR, P=0.002; surgical AVR, P=0.026 [all-cause mortality]). Every 1% increase in left ventricular myocardial scar burden was associated with 11% higher all-cause mortality hazard (HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.05-1.17; P<0.001) and 8% higher cardiovascular mortality hazard (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.01-1.17; P<0.001).
Conclusions: In patients with severe aortic stenosis, late gadolinium enhancement on cardiovascular magnetic resonance was independently associated with mortality; its presence was associated with a 2-fold higher late mortality.
Keywords: aortic valve stenosis; magnetic resonance imaging; mortality; myocardium.
Figures

Comment in
-
Not Too Little and Not Too Late.Circulation. 2018 Oct 30;138(18):1948-1950. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036600. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 30372139 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nkomo VT, Gardin JM, Skelton TN, Gottdiener JS, Scott CG, Enriquez-Sarano M. Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Lancet. 2006;368:1005–1011. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69208-8. - PubMed
-
- Dweck MR, Boon NA, Newby DE. Calcific aortic stenosis: a disease of the valve and the myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1854–1863. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.02.093. - PubMed
-
- Carabello BA, Paulus WJ. Aortic stenosis. Lancet. 2009;373:956–966. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60211-7. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner H, Falk V, Bax JJ, De Bonis M, Hamm C, Holm PJ, Iung B, Lancellotti P, Lansac E, Rodriguez Muñoz D, Rosenhek R, Sjögren J, Tornos Mas P, Vahanian A, Walther T, Wendler O, Windecker S, Zamorano JL ESC Scientific Document Group. 2017 ESC/EACTS guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:2739–2791. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx391. - PubMed
-
- Weidemann F, Herrmann S, Störk S, Niemann M, Frantz S, Lange V, Beer M, Gattenlöhner S, Voelker W, Ertl G, Strotmann JM. Impact of myocardial fibrosis in patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis. Circulation. 2009;120:577–584. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.847772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

