Squamous cell carcinoma arising in hypertrophic lichen planus
- PMID: 30002207
- PMCID: PMC6047711
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-224044
Squamous cell carcinoma arising in hypertrophic lichen planus
Abstract
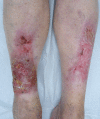
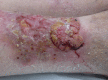
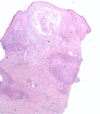
Hypertrophic lichen planus (HLP) is a chronic T-cell-mediated inflammatory disease characterised by pruritic hypertrophic or verrucous plaques on the lower limbs. We report a case of an 87-year-old woman with a 12-year history of HLP on both lower legs presenting with malignant transformation of one lesion into a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Malignancy developing in cutaneous lichen planus is rare, with less than 50 cases reported in the literature. This case highlights the need to be aware of suspicious changes in long-standing HLP to allow early detection of a developing SCC.
Keywords: dermatology; oncology; skin cancer.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2018. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Widely metastatic squamous cell carcinoma originating from malignant transformation of hypertrophic lichen planus in a 24-year-old woman: case report and review of the literature.Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 May-Jun;32(3):e98-101. doi: 10.1111/pde.12549. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25739384
-
Expression of p16 in Hypertrophic Lichen Planus.Am J Dermatopathol. 2025 Jun 1;47(6):448-452. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000002940. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Am J Dermatopathol. 2025. PMID: 39912658
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in Hypertrophic Lichen Planus: A Review and Analysis of 38 Cases.Dermatol Surg. 2015 Dec;41(12):1411-8. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000565. Dermatol Surg. 2015. PMID: 26551772 Review.
-
Twice malignant transformation of hypertrophic lichen planus.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2012;19(4):787-9. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2012. PMID: 23311808
-
[Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma complicating hypertrophic lichen planus. Three case reports and review of the literature].Hautarzt. 2011 Jan;62(1):40-5. doi: 10.1007/s00105-010-1961-4. Hautarzt. 2011. PMID: 20664992 Review. German.
Cited by
-
To treat or not to treat: PD-L1 inhibitor-induced keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 May;315(4):903-915. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02468-3. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 36394634
-
Current Understanding of Flavonoids in Cancer Therapy and Prevention.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 27;13(4):481. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040481. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertrophic Lichen Planus and Hypertrophic Skin Lesions Associated with Histological Lichenoid Infiltrate: A Case Report and Literature Review.Dermatopathology (Basel). 2025 Feb 25;12(1):8. doi: 10.3390/dermatopathology12010008. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Giant Squamous Cell Carcinoma on Chronic Lichen Planus on the Ankle - A Case Report and Short Literature Review.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Aug 19;7(18):3061-3063. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.553. eCollection 2019 Sep 30. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31850123 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent bilateral cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising within hypertrophic lichen planus with metastasis while on cemiplimab.JAAD Case Rep. 2022 Sep 5;29:55-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.08.046. eCollection 2022 Nov. JAAD Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36193242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JJ, Schaffer JV, et al. . Dermatology. 3rd edn London: Elsevier, 2012.
-
- Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelöf B. Lichen planus and malignancy. An epidemiologic study of 2071 patients and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol 1991;127:1684–8. - PubMed
-
- Bonnekoh B, Kuhn A. [Squamous epithelial cancer in lichen ruber hypertrophicus--a case report with a review of the literature]. Z Hautkr 1986;61:394–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
