Integrating endocannabinoid signaling in the regulation of anxiety and depression
- PMID: 30002489
- PMCID: PMC6460364
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-018-0051-5
Integrating endocannabinoid signaling in the regulation of anxiety and depression
Abstract
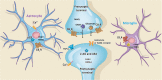
Brain endogenous cannabinoid (eCB) signaling seems to harmonize appropriate behavioral responses, which are essential for the organism's long-term viability and homeostasis. Dysregulation of eCB signaling contributes to negative emotional states and increased stress responses. An understanding of the underlying neural cell populations and neural circuit regulation will enable the development of therapeutic strategies to mitigate behavioral maladaptation and provide insight into the influence of eCB on the neural circuits involved in anxiety and depression. This review focuses on recent evidence that has added a new layer of complexity to the idea of targeting the eCB system for therapeutic benefits in neuropsychiatric disease and on the future research direction of neural circuit modulation.
Keywords: anxiety; cannabinoid 1 receptor (CB1R); depression; endocannabinoid (eCB); neural circuits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

