Disseminated Histoplasmosis as AIDS-presentation. Case Report and Comprehensive Review of Current Literature
- PMID: 30002796
- PMCID: PMC6039081
- DOI: 10.4084/MJHID.2018.040
Disseminated Histoplasmosis as AIDS-presentation. Case Report and Comprehensive Review of Current Literature
Abstract
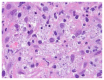
Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis (PDH) is an AIDS-defining illness with a high lethality rate if not promptly treated. The wide range of its possible clinical manifestations represents the main barrier to diagnosis in non-endemic countries. Here we present a case of PDH with haemophagocytic syndrome in a newly diagnosed HIV patient and a comprehensive review of disseminated histoplasmosis focused on epidemiology, clinical features, diagnostic tools and treatment options in HIV-infected patients.
Keywords: AIDS; Disseminated histoplasmosis; HIV; Histoplasma capsulatum.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

