Long scan depth optical coherence tomography on imaging accommodation: impact of enhanced axial resolution, signal-to-noise ratio and speed
- PMID: 30003116
- PMCID: PMC6036665
- DOI: 10.1186/s40662-018-0111-4
Long scan depth optical coherence tomography on imaging accommodation: impact of enhanced axial resolution, signal-to-noise ratio and speed
Abstract
Background: Spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) was a useful tool to study accommodation in human eye, but the maximum image depth is limited due to the decreased signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In this study, improving optical resolutions, speeds and the SNR were achieved by custom built SD-OCT, and the evaluation of the impact of the improvement during accommodation was investigated.
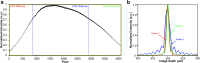
Methods: Three systems with different spectrometer designs, including two Charge Coupled Device (CCD) cameras and one Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor (CMOS) camera, were tested. We measured the point spread functions of a mirror at different positions to obtain the axial resolution and the SNR of three OCT systems powered with a light source with a 50 nm bandwidth, centered at a wavelength of 840 nm. Two normal subjects, aged 26 and 47, respectively, and one 75-year-old patient with an intraocular lens implanted were imaged.
Results: The results indicated that spectrometers using cameras with 4096 camera pixels optimized the axial resolutions, due to the use of the full spectrum provided by the light source. The CCD camera system with 4096 pixels had the highest SNR and the best image quality. The system with the CMOS camera with 4096 pixels had the highest speed but had a compromised SNR compared to the CCD camera with 4096 pixels.
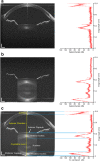
Conclusions: Using these three OCT systems, we imaged the anterior segment of the human eye before and after accommodation, which showed similar results among the different systems. The system using the CMOS camera with an ultra-long scan depth, high resolution and high scan speed exhibited the best overall performance and therefore was recommended for imaging real-time accommodation.
Keywords: Accommodation; Anterior segment; Axial resolution; Optical coherence tomography; Signal-to-noise ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was approved by the institutional review board for human research at the University of Miami. Informed consent was obtained from each subject and all patients were treated in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.Informed consent was obtained from each subject.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Koretz JF, Cook CA, Kaufman PL. Accommodation and presbyopia in the human eye. Changes in the anterior segment and crystalline lens with focus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38(3):569–578. - PubMed
-
- von Helmholtz H. Uber die akkommodation des auges. Archiv Ophthalmol. 1855;1:1–74.
-
- Dubbelman M, Van der Heijde GL, Weeber HA. Change in shape of the aging human crystalline lens with accommodation. Vision Res. 2005;45(1):117–32. - PubMed
-
- Hermans EA, Pouwels PJ, Dubbelman M, Kuijer JP, van der Heijde RG, Heethaar RM. Constant volume of the human lens and decrease in surface area of the capsular bag during accommodation: an MRI and Scheimpflug study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50(1):281–289. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2124. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

