Cytokine-specific Neurograms in the Sensory Vagus Nerve
- PMID: 30003120
- PMCID: PMC6039192
Cytokine-specific Neurograms in the Sensory Vagus Nerve
Abstract
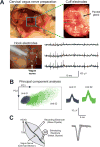
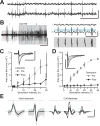
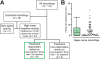
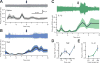
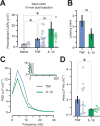
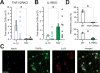
The axons of the sensory, or afferent, vagus nerve transmit action potentials to the central nervous system in response to changes in the body's metabolic and physiological status. Recent advances in identifying neural circuits that regulate immune responses to infection, inflammation and injury have revealed that vagus nerve signals regulate the release of cytokines and other factors produced by macrophages. Here we record compound action potentials in the cervical vagus nerve of adult mice and reveal the specific activity that occurs following administration of the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β). Importantly, the afferent vagus neurograms generated by TNF exposure are abolished in double knockout mice lacking TNF receptors 1 and 2 (TNF-R1/2KO), whereas IL-1β-specific neurograms are eliminated in knockout mice lacking IL-1β receptor (IL-1RKO). Conversely, TNF neurograms are preserved in IL-1RKO mice, and IL-1β neurograms are unchanged in TNF-R1/2KO mice. Analysis of the temporal dynamics and power spectral characteristics of afferent vagus neurograms for TNF and IL-1β reveals cytokine-selective signals. The nodose ganglion contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons whose axons run through the vagus nerve. The nodose neurons express receptors for TNF and IL-1β, and we show that exposing them to TNF and IL-1β significantly stimulates their calcium uptake. Together these results indicate that afferent vagus signals in response to cytokines provide a basic model of nervous system sensing of immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE The authors declare that they have no competing interests as defined by Bioelectronic Medicine, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and discussion reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of cytokine-specific sensory neural signals by decoding murine vagus nerve activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 22;115(21):E4843-E4852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1719083115. Epub 2018 May 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29735654 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin-1-expressing vagus nerve fibers mediate IL-1β induced hypothermia and reflex anti-inflammatory responses.Mol Med. 2023 Jan 18;29(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00590-6. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36650454 Free PMC article.
-
Vagal afferent fibers contribute to the anti-inflammatory reactions by vagus nerve stimulation in concanavalin A model of hepatitis in rats.Mol Med. 2020 Dec 3;26(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00247-2. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33272194 Free PMC article.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation: Novel concept for the treatment of glioblastoma and solid cancers by cytokine (interleukin-6) reduction, attenuating the SASP, enhancing tumor immunity.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Sep 17;42:100859. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100859. eCollection 2024 Dec. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 39512605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanisms of immune-to-brain communication in inflammation as a drug target.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002 Sep;1(3):257-62. doi: 10.2174/1568010023344599. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2002. PMID: 14561190 Review.
Cited by
-
The carotid body: A novel key player in neuroimmune interactions.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 24;13:1033774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1033774. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroimmune interactions and kidney disease.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2019 Sep 30;38(3):282-294. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.19.014. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 31422643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of cytokine-specific sensory neural signals by decoding murine vagus nerve activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 22;115(21):E4843-E4852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1719083115. Epub 2018 May 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29735654 Free PMC article.
-
Computational models of compound nerve action potentials: Efficient filter-based methods to quantify effects of tissue conductivities, conduction distance, and nerve fiber parameters.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Mar 1;20(3):e1011833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011833. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38427699 Free PMC article.
-
Neural representation of cytokines by vagal sensory neurons.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 24;16(1):3840. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59248-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40268933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tracey KJ. The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 2002;420:853–59. - PubMed
-
- Hansen MK, O’Connor KA, Goehler LE, Watkins LR, Maier SF. The contribution of the vagus nerve in interleukin-1beta–induced fever is dependent on dose. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;280:R929–34. - PubMed
-
- Watkins LR, Goehler LE, Relton JK, et al. Blockade of interleukin-1 induced hyperthermia by subdiaphragmatic vagotomy: evidence for vagal mediation of immune-brain communication. Neurosci Lett. 1995;183:27–31. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
