Intravenous Ketamine for Adolescents with Treatment-Resistant Depression: An Open-Label Study
- PMID: 30004254
- PMCID: PMC6154760
- DOI: 10.1089/cap.2018.0030
Intravenous Ketamine for Adolescents with Treatment-Resistant Depression: An Open-Label Study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Intravenous Ketamine for Adolescents with Treatment-Resistant Depression: An Open-Label Study, by Cullen KR, Amatya P, Roback MG, Albott CS, Westlund Schreiner M, Ren Y, Eberly LE, Carstedt P, Samikoglu A, Gunlicks-Stoessel M, Reigstad K, Horek N, Tye S, Lim KO, Klimes-Dougan B. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 2018;28(7):437-444. DOI: 10.1089/cap.2018.0030.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2019 Feb;29(1):77. doi: 10.1089/cap.2018.0030.correx. Epub 2018 Dec 26. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30585735 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Novel interventions for treatment-resistant depression (TRD) in adolescents are urgently needed. Ketamine has been studied in adults with TRD, but little information is available for adolescents. This study investigated efficacy and tolerability of intravenous ketamine in adolescents with TRD, and explored clinical response predictors.
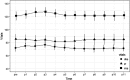
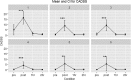
Methods: Adolescents, 12-18 years of age, with TRD (failure to respond to two previous antidepressant trials) were administered six ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) infusions over 2 weeks. Clinical response was defined as a 50% decrease in Children's Depression Rating Scale-Revised (CDRS-R); remission was CDRS-R score ≤28. Tolerability assessment included monitoring vital signs and dissociative symptoms using the Clinician-Administered Dissociative States Scale (CADSS).
Results: Thirteen participants (mean age 16.9 years, range 14.5-18.8 years, eight biologically male) completed the protocol. Average decrease in CDRS-R was 42.5% (p = 0.0004). Five (38%) adolescents met criteria for clinical response. Three responders showed sustained remission at 6-week follow-up; relapse occurred within 2 weeks for the other two responders. Ketamine infusions were generally well tolerated; dissociative symptoms and hemodynamic symptoms were transient. Higher dose was a significant predictor of treatment response.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate the potential role for ketamine in treating adolescents with TRD. Limitations include the open-label design and small sample; future research addressing these issues are needed to confirm these results. Additionally, evidence suggested a dose-response relationship; future studies are needed to optimize dose. Finally, questions remain regarding the long-term safety of ketamine as a depression treatment; more information is needed before broader clinical use.
Keywords: adolescent; depression; ketamine; treatment-resistant.
Figures
References
-
- aan het Rot M, Collins KA, Murrough JW, Perez AM, Reich DL, Charney DS, Mathew SJ: Safety and efficacy of repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 67:139–145, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Allen NB, Hetrick SE, Simmons JG, Hickie IB: Early intervention for depressive disorders in young people: The opportunity and the (lack of) evidence. Med J Aust 187:S15–S17, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Krystal JH: Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Bhatt M, Johnson DW, Chan J, Taljaard M, Barrowman N, Farion KJ, Ali S, Beno S, Dixon A, McTimoney CM, Dubrovsky AS, Sourial N, Roback MG; Sedation Safety Study Group of Pediatric Emergency Research Canada (PERC): Risk factors for adverse events in emergency department procedural sedation for children. JAMA Pediatr 171:957–964, 2017 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Putnam FW, Southwick SM, Marmar C, Charney DS, Mazure CM: Measurement of dissociative states with the Clinician-Administered Dissociative States Scale (CADSS). J Trauma Stress 11:125–136, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

