LAG-3 Inhibitory Receptor Expression Identifies Immunosuppressive Natural Regulatory Plasma Cells
- PMID: 30005826
- PMCID: PMC6057275
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.06.007
LAG-3 Inhibitory Receptor Expression Identifies Immunosuppressive Natural Regulatory Plasma Cells
Abstract
B lymphocytes can suppress immunity through interleukin (IL)-10 production in infectious, autoimmune, and malignant diseases. Here, we have identified a natural plasma cell subset that distinctively expresses the inhibitory receptor LAG-3 and mediates this function in vivo. These plasma cells also express the inhibitory receptors CD200, PD-L1, and PD-L2. They develop from various B cell subsets in a B cell receptor (BCR)-dependent manner independently of microbiota in naive mice. After challenge they upregulate IL-10 expression via a Toll-like receptor-driven mechanism within hours and without proliferating. This function is associated with a unique transcriptome and epigenome, including the lowest amount of DNA methylation at the Il10 locus compared to other B cell subsets. Their augmented accumulation in naive mutant mice with increased BCR signaling correlates with the inhibition of memory T cell formation and vaccine efficacy after challenge. These natural regulatory plasma cells may be of broad relevance for disease intervention.
Keywords: B cells; BCR; CD72; LAG-3; TLR; checkpoint receptor; immune regulation; infection; interleukin-10; natural regulatory plasma cell; plasma cells.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

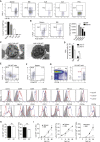


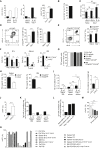

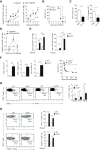
Comment in
-
Natural regulatory plasma cells.Nat Rev Immunol. 2018 Sep;18(9):540-541. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0057-8. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30108318 No abstract available.
References
-
- Blair P.A., Chavez-Rueda K.A., Evans J.G., Shlomchik M.J., Eddaoudi A., Isenberg D.A., Ehrenstein M.R., Mauri C. Selective targeting of B cells with agonistic anti-CD40 is an efficacious strategy for the generation of induced regulatory T2-like B cells and for the suppression of lupus in MRL/lpr mice. J. Immunol. 2009;182:3492–3502. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

