Co-expression of CD39 and CD103 identifies tumor-reactive CD8 T cells in human solid tumors
- PMID: 30006565
- PMCID: PMC6045647
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05072-0
Co-expression of CD39 and CD103 identifies tumor-reactive CD8 T cells in human solid tumors
Abstract
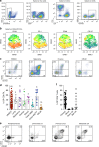
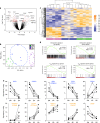
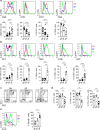
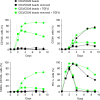
Identifying tumor antigen-specific T cells from cancer patients has important implications for immunotherapy diagnostics and therapeutics. Here, we show that CD103+CD39+ tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cells (CD8 TIL) are enriched for tumor-reactive cells both in primary and metastatic tumors. This CD8 TIL subset is found across six different malignancies and displays an exhausted tissue-resident memory phenotype. CD103+CD39+ CD8 TILs have a distinct T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire, with T-cell clones expanded in the tumor but present at low frequencies in the periphery. CD103+CD39+ CD8 TILs also efficiently kill autologous tumor cells in a MHC-class I-dependent manner. Finally, higher frequencies of CD103+CD39+ CD8 TILs in patients with head and neck cancer are associated with better overall survival. Our data thus describe an approach for detecting tumor-reactive CD8 TILs that will help define mechanisms of existing immunotherapy treatments, and may lead to future adoptive T-cell cancer therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
T.D., R.D., R.M. and A.D.W. disclose that they have submitted a patent regarding therapeutic and diagnostic use of these cells in cancer patients. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
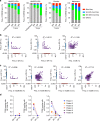
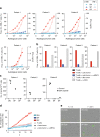
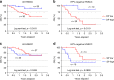
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

