Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination
- PMID: 30006589
- PMCID: PMC6045662
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05114-7
Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination
Abstract
Severe liver abscess infections caused by hypervirulent clonal-group CG23 Klebsiella pneumoniae have been increasingly reported since the mid-1980s. Strains typically possess several virulence factors including an integrative, conjugative element ICEKp encoding the siderophore yersiniabactin and genotoxin colibactin. Here we investigate CG23's evolutionary history, showing several deep-branching sublineages associated with distinct ICEKp acquisitions. Over 80% of liver abscess isolates belong to sublineage CG23-I, which emerged in ~1928 following acquisition of ICEKp10 (encoding yersiniabactin and colibactin), and then disseminated globally within the human population. CG23-I's distinguishing feature is the colibactin synthesis locus, which reportedly promotes gut colonisation and metastatic infection in murine models. These data show circulation of CG23 K. pneumoniae decades before the liver abscess epidemic was first recognised, and provide a framework for future epidemiological and experimental studies of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae. To support such studies we present an open access, completely sequenced CG23-I human liver abscess isolate, SGH10.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

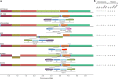
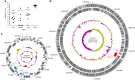
References
-
- Liao CH, Huang YT, Chang CY, Hsu HS, Hsueh PR. Capsular serotypes and multilocus sequence types of bacteremic Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates associated with different types of infections. Eur J ClinMicrobiol. Infect. Dis. 2014;33:365–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

