Non-microsurgical skin flaps for reconstruction of difficult wounds in distal leg and foot
- PMID: 30007533
- PMCID: PMC6085275
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2017.08.009
Non-microsurgical skin flaps for reconstruction of difficult wounds in distal leg and foot
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Declaration of Competing Interest statements in previously published articles.Chin J Traumatol. 2025 Sep;28(5):388. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2020.12.005. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Chin J Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 33371992 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
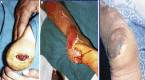
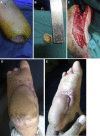
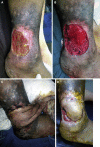
Purpose: To express the versatility of a variety of non-microsurgical skin flaps used for coverage of difficult wounds in the lower third of the leg and the foot over 4 years period. Five kinds of flaps were used. Each flap was presented with detailed information regarding indication, blood supply, skin territory and technique.
Methods: Altogether 26 patients underwent lower leg reconstruction were included in this study. The reconstructive procedures applied five flaps, respectively distally based posterior tibial artery perforator flap (n = 8), distally based peroneal artery perforator flap (n = 4), distally based sural flap (n = 6), medial planter artery flap (n = 2) and cross leg flaps (n = 6).
Results: In all cases, there were no signs of osteomyelitis of underlying bones or discharge from the undersurface of the flaps. Fat necrosis occurred at the distal end of posterior tibial artery perforator flap in one female patient. The two cases of medial planter artery flap showed excellent healing with closure of donor site primarily. One cross leg flap had distal necrosis.
Conclusion: Would at lower third of leg can be efficiently covered by posterior tibial, peroneal artery and sural flaps. Heel can be best covered by nearby tissues such as medial planter flap. In presence of vascular compromise of the affected limb or exposure of dorsum of foot, cross leg flap can be used.
Keywords: Cross leg flaps; Foot; Local flaps; Lower third of leg.
Copyright © 2018 Daping Hospital and the Research Institute of Surgery of the Third Military Medical University. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Ong Y.S., Levin L.S. Lower limb salvage in trauma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:582–588. - PubMed
-
- Pinsolle V., Reau A.F., Pelissier P. Soft-tissue reconstruction of the distal lower leg and foot: are free flaps the only choice? Review of 215 cases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg. 2006;59:912–917. discussion 918. - PubMed
-
- Hallock G.G. Distally based flaps for skin coverage of the foot and ankle. Foot Ankle Int. 1996;17:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Parrett B.M., Talbot S.G., Pribaz J.J. A review of local and regional flaps for distal leg reconstruction. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2009;25:445–455. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
