Recurrent inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the lung: FDG PET/CT scan findings
- PMID: 30007906
- PMCID: PMC6047701
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224373
Recurrent inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the lung: FDG PET/CT scan findings
Abstract
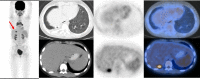
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (IMT) is a rare neoplasm, occurring most often in children and young adults. IMTs have intermediate biological behaviour with the chance of local invasion, recurrence and even distant metastasis. Wide range of clinical presentations makes the precise diagnosis of IMT more challenging. The best method for definitive diagnosis is tissue biopsy and newer imaging modalities including fleurodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/CT are useful tools in detection of disease recurrence or distant metastasis. Complete surgical resection is the best-known treatment for this tumour. Here we are presenting an IMT case in a 12-year-old girl in which her recurrent pulmonary IMT was diagnosed based on FDG PET/CT findings and referred for further salvage treatment. Overall imaging modalities are not specific, but PET/CT scan can be useful tool for evaluation of IMT regarding initial staging and restaging to assess treatment response and recurrence.
Keywords: oncology; radiology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2018. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
