The Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylation Complex Modulates Chromatin Structure at Sites of Active Transcription to Fine-Tune Gene Expression
- PMID: 30008319
- PMCID: PMC6039721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.003
The Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylation Complex Modulates Chromatin Structure at Sites of Active Transcription to Fine-Tune Gene Expression
Abstract
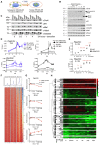
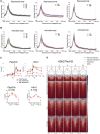
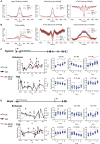
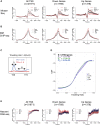
Chromatin remodeling complexes play essential roles in metazoan development through widespread control of gene expression, but the precise molecular mechanisms by which they do this in vivo remain ill defined. Using an inducible system with fine temporal resolution, we show that the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylation (NuRD) complex controls chromatin architecture and the protein binding repertoire at regulatory regions during cell state transitions. This is primarily exerted through its nucleosome remodeling activity while deacetylation at H3K27 follows changes in gene expression. Additionally, NuRD activity influences association of RNA polymerase II at transcription start sites and subsequent nascent transcript production, thereby guiding the establishment of lineage-appropriate transcriptional programs. These findings provide a detailed molecular picture of genome-wide modulation of lineage-specific transcription by an essential chromatin remodeling complex as well as insight into the orchestration of molecular events involved in transcriptional transitions in vivo. VIDEO ABSTRACT.
Keywords: Mediator; NuRD; RNA polymerase II; chromatin; embryonic stem cells; enhancer; transcription; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Gene dimmer switch.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Sep;19(9):545. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0038-6. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29993030 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aguilera C., Nakagawa K., Sancho R., Chakraborty A., Hendrich B., Behrens A. c-Jun N-terminal phosphorylation antagonises recruitment of the Mbd3/NuRD repressor complex. Nature. 2011;469:231–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

