Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Liver Diseases
- PMID: 30008587
- PMCID: PMC6036079
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.24755
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Liver Diseases
Abstract
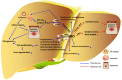
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is an efficient therapeutic option to improve progress of lots of diseases especially hypoxia-related injuries, and has been clinically established as a wide-used therapy for patients with carbon monoxide poisoning, decompression sickness, arterial gas embolism, problematic wound, and so on. In the liver, most studies positively evaluated HBOT as a potential therapeutic option for liver transplantation, acute liver injury, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, fibrosis and cancer, especially for hepatic artery thrombosis. This might mainly attribute to the anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation of HBOT. However, some controversies are existed, possibly due to hyperbaric oxygen toxicity. This review summarizes the current understandings of the role of HBOT in liver diseases and hepatic regeneration. Future understanding of HBOT in clinical trials and its in-depth mechanisms may contribute to the development of this novel adjuvant strategy for clinical therapy of liver diseases.
Keywords: hyperbaric oxygen; liver diseases; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Savage S. New medical therapy: hyperbarics. Tennessee medicine: journal of the Tennessee Medical Association. 2010;103:39–40. - PubMed
-
- Tibbles PM, Edelsberg JS. Hyperbaric-oxygen therapy. The New England journal of medicine. 1996;334:1642–8. - PubMed
-
- Zarrinpar A, Busuttil RW. Liver transplantation: past, present and future. Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2013;10:434–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

