miR-210 promotes human osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion by targeting FGFRL1
- PMID: 30008923
- PMCID: PMC6036426
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8939
miR-210 promotes human osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion by targeting FGFRL1
Abstract
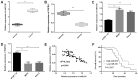
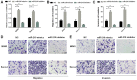
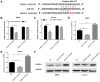
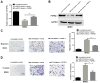
Osteosarcoma is a common bone tumor and a frequently occuring cancer-associated threat to children. Notably, the prognosis of osteosarcoma is very poor when it is diagnosed with metastasis. A growing number of studies have indicated that various microRNAs (miRs) serve important regulatory roles in the pathogeny of different types of cancer. However, the functions of miR-210 in osteosarcoma need to be elucidated comprehensively. The aim of the present study was to investigate the potential roles of miR-210 in osteosarcoma by targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1). Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction results revealed that the expression of miR-210 was highly elevated while FGFRL1 expression was reduced inversely in osteosarcoma tissues compared with matched normal tissues. The results of Transwell assays showed that miR-210 promoted osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion. Furthermore, the luciferase reporter assay results suggested that miR-210 could directly bind to FGFRL1 in osteosarcoma cells. In addition, the present findings demonstrated that miR-210 could negatively regulate FGFRL1 expression by targeting the 3'untranslated region. In conclusion, the findings of the present study suggested that miR-210 exerted tumor carcinogenic functions in osteosarcoma by targeting FGFRL1. The findings of this study demonstrated that FGFRL1 was a direct target of miR-210 in osteosarcoma involved in the promoting functions mediated by miR-210 in the invasion and migration of osteosarcoma, suggesting that miR-210/FGFRL1 may be promising for discovering diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for the therapies of osteosarcoma.
Keywords: FGFRL1; human osteosarcoma; invasion; miR-210; migration.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
