Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men's Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization
- PMID: 30009140
- PMCID: PMC6010824
Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men's Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization
Abstract
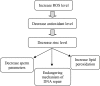
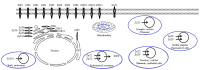
Zinc (Zn) is the second most abundant trace element in human, which can't be stored in the body, thus regular dietary intake is required. This review explained the physiological and pathogenesis roles of zinc in men's health and its potentials in germination, quality of sperm, and fertilization. Our investigation showed that Zn contained many unique properties in human, especially males. The antioxidant quality is one of them. Also, the increased reactive oxygen species levels in the seminal plasma of men who are both infertile and smokers influence the Zn content of seminal plasma in a way that physiology of spermatozoa can be affected as well. Moreover, Zn acts as a toxic repercussionagainst heavy metals and cigarette inflammatory agents. Zinc as a hormone balancer helps hormones such as testosterone, prostate and sexual healthand functions as an antibacterial agent in men's urea system. It plays a role in epithelial integrity, showing that Zn is essential for maintaining the lining of the reproductive organs and may have a regulative role in the progress of capacitation and acrosome reaction. In contrast, Zn deficiency impedes spermatogenesis and is a reason for sperm abnormalities and has a negative effect on serum testosterone concentration. Based on these findings, Zn microelement is very essential for male fertility. It could be considered as a nutrient marker with many potentials in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of male infertility.
Keywords: Germination; Male fertility; Microelement; ROS; Sperm parameters; Zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. Financial Disclosure: The authors declared no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yuyan L, Junqing W, Wei Y, Weijin Z, Ersheng G. Are serum zinc and copper levels related to semen quality? Fertil Steril. 2008;89(4):1008–11. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources