Battle of GLP-1 delivery technologies
- PMID: 30009885
- PMCID: PMC6843995
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.07.009
Battle of GLP-1 delivery technologies
Abstract
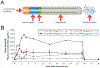
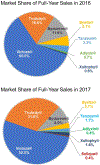
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) belong to an important therapeutic class for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Six GLP-1 RAs, each utilizing a unique drug delivery strategy, are now approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and additional, novel GLP-1 RAs are still under development, making for a crowded marketplace and fierce competition among the manufacturers of these products. As rapid elimination is a major challenge for clinical application of GLP-1 RAs, various half-life extension strategies have been successfully employed including sequential modification, attachment of fatty-acid to peptide, fusion with human serum albumin, fusion with the fragment crystallizable (Fc) region of a monoclonal antibody, sustained drug delivery systems, and PEGylation. In this review, we discuss the scientific rationale of the various half-life extension strategies used for GLP-1 RA development. By analyzing and comparing different approved GLP-1 RAs and those in development, we focus on assessing how half-life extending strategies impact the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, patient usability and ultimately, the commercial success of GLP-1 RA products. We also anticipate future GLP-1 RA development trends. Since similar drug delivery strategies are also applied for developing other therapeutic peptides, we expect this case study of GLP-1 RAs will provide generalizable concepts for the rational design of therapeutic peptides products with extended duration of action.
Keywords: Albumin fusion; Exenatide; Fatty acid conjugate; Fc fusion; GLP-1 receptor agonist; Half-life; Peptide delivery; Pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- B.I.D.F. Brussels, International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th edn., 2017.
-
- Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE, Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035, Diabetes research and clinical practice, 103 (2014) 137–149. - PubMed
-
- G. International Diabetes Federation Guideline Development, Global guideline for type 2 diabetes, Diabetes research and clinical practice, 104 (2014) 1–52. - PubMed
-
- Ali MK, Bullard KM, Gregg EW, Achievement of goals in U.S. Diabetes Care, 1999–2010, The New England journal of medicine, 369 (2013) 287–288. - PubMed
-
- Marathe PH, Gao HX, Close KL, American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2017, Journal of diabetes, 9 (2017) 320–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

