18F-FDG PET for Prediction of Conversion to Alzheimer's Disease Dementia in People with Mild Cognitive Impairment: An Updated Systematic Review of Test Accuracy
- PMID: 30010119
- PMCID: PMC6218118
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-171125
18F-FDG PET for Prediction of Conversion to Alzheimer's Disease Dementia in People with Mild Cognitive Impairment: An Updated Systematic Review of Test Accuracy
Abstract
Background: A previous Cochrane systematic review concluded there is insufficient evidence to support the routine use of 18F-FDG PET in clinical practice in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Objectives: To update the evidence and reassess the accuracy of 18F-FDG-PET for detecting people with MCI at baseline who would clinically convert to Alzheimer's disease (AD) dementia at follow-up.
Methods: A systematic review including comprehensive search of electronic databases from January 2013 to July 2017, to update original searches (1999 to 2013). All key review steps, including quality assessment using QUADAS 2, were performed independently and blindly by two review authors. Meta-analysis could not be conducted due to heterogeneity across studies.
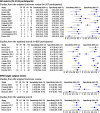
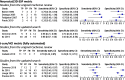
Results: When all included studies were examined across all semi-quantitative and quantitative metrics, exploratory analysis for conversion of MCI to AD dementia (n = 24) showed highly variable accuracy; half the studies failed to meet four or more of the seven sets of QUADAS 2 criteria. Variable accuracy for all metrics was also found across eleven newly included studies published in the last 5 years (range: sensitivity 56-100%, specificity 24-100%). The most consistently high sensitivity and specificity values (approximately ≥80%) were reported for the sc-SPM (single case statistical parametric mapping) metric in 6 out of 8 studies.
Conclusion: Systematic and comprehensive assessment of studies of 18FDG-PET for prediction of conversion from MCI to AD dementia reveals many studies have methodological limitations according to Cochrane diagnostic test accuracy gold standards, and shows accuracy remains highly variable, including in the most recent studies. There is some evidence, however, of higher and more consistent accuracy in studies using computer aided metrics, such as sc-SPM, in specialized clinical settings. Robust, methodologically sound prospective longitudinal cohort studies with long (≥5 years) follow-up, larger consecutive samples, and defined baseline threshold(s) are needed to test these promising results. Further evidence of the clinical validity and utility of 18F-FDG PET in people with MCI is needed.
Keywords: 18F-FDG PET; Accuracy; Alzheimer’s disease dementia; conversion; mild cognitive impairment; test predictive value.
Figures


References
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services TaskForce on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34, 939–944. - PubMed
-
- Prince M, Bryce R, Ferri C (2011) World Alzheimer Report 2011: The benefits of early diagnosis and intervention. Alzheimer Disease International https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2011.pdf, accessed on March 28, 2017.
-
- Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 256, 183–194. - PubMed
-
- Bruscoli M, Lovestone S (2004) Is MCI really just early dementia? A systematic review of conversion studies. Int Psychogeriatr 16, 129–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

