Therapeutic Agents with AHR Inhibiting and NRF2 Activating Activity for Managing Chloracne
- PMID: 30011787
- PMCID: PMC6071176
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox7070090
Therapeutic Agents with AHR Inhibiting and NRF2 Activating Activity for Managing Chloracne
Abstract
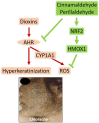
Chloracne is the major skin symptom caused by dioxin intoxication. Dioxin activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)⁻cytochrome p450 1A1 (CYP1A1) system, generates oxidative stress, and induces hyperkeratinization of keratinocytes and sebocytes leading to chloracne. Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (NRF2) is a master switch that induces the expression of various antioxidative enzymes, such as heme oxygenase-1. Cinnamaldehyde is an antioxidant phytochemical that inhibits AHR⁻CYP1A1 signaling and activates the NRF2⁻antioxidative axis. The cinnamaldehyde-containing Kampo herbal medicine Keishibukuryogan is capable of improving chloracne in Yusho patients who are highly contaminated with dioxin. Agents with dual functions in promoting AHR⁻CYP1A1 inhibition and NRF2 activation may be useful for managing dioxin-related health hazards.
Keywords: Yusho; aryl hydrocarbon receptor; chloracne; dioxin; heme oxygenase-1; nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tsuji G., Takahara M., Uchi H., Takeuchi S., Mitoma C., Moroi Y., Furue M. An environmental contaminant, benzo(a)pyrene, induces oxidative stress-mediated interleukin-8 production in human keratinocytes via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011;62:42–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.10.017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

