Study on the Photoluminescent and Thermal Properties of Zinc Complexes with a N₆O₄ Macrocyclic Ligand
- PMID: 30012984
- PMCID: PMC6100202
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23071735
Study on the Photoluminescent and Thermal Properties of Zinc Complexes with a N₆O₄ Macrocyclic Ligand
Abstract
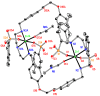
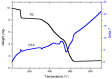
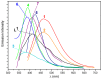
Reactions between a N₆O₄ macrocyclic ligand (L¹) and several Zn(II) salts (trifluoromethane sulfonate, p-toluenesulfonate, acetate, benzoate, o-, m- or p-hydroxybenzoate) led to the formation of seven complexes, [Zn₂L¹ (DMSO)₄](OSO₂CF₃)₄ (1), [Zn₂(p-OSO₂PhCH₃)₄L¹] (2), [Zn₂(OCOCH₃)₄L¹] (3), [Zn₂(OCOPh)₄L¹] (4), [Zn₂(o-OCOPhOH)₄L¹] (5), [Zn₂(m-OCOPhOH)₄ L¹] (6) and [Zn₂(p-OCOPhOH)₄ L¹] (7), which were characterized by elemental analysis, ¹H-NMR, 13C-NMR, IR, fluorescence spectroscopies and single crystal X-ray diffraction. In 1, the Zn atom is pentacoordinated with a N₃O₂ irregular trigonal bipyramidal coordination environment, like the geometries in compounds 3⁻7, whereas in structure 2 the metal atom is envisaged as possessing a distorted N₃O₃ octahedronal environment. All the compounds show interesting photoluminescent properties in solid states and solutions in DMF and DMSO, which are reported along with their TG-DTA thermal decomposition processes, UV-vis absorption spectroscopy and fluorescence quantum yields in DMF and DMSO.
Keywords: macrocyclic ligand; photoluminescent properties; thermal properties; zinc complexes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








References
-
- Nelson J., Mckee V., Morgan G. Coordination chemistry of azacryptands. Prog. Inorg. Chem. 1998;47:167–316. doi: 10.1002/9780470166482.ch2. - DOI
-
- Geoghegan P., O’Leary P. Hydroxyamide-based ligands and their use in the asymmetric catalysis of key organic transformations. ACS Catal. 2012;2:573–591. doi: 10.1021/cs300111b. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

