Establishing catheter-related bloodstream infection surveillance to drive improvement
- PMID: 30013620
- PMCID: PMC6039910
- DOI: 10.1177/1757177418767759
Establishing catheter-related bloodstream infection surveillance to drive improvement
Abstract
Background: Catheter-related blood stream infections (CRBSI) are an important complication of central venous access devices but are often poorly measured. This article describes the journey of one hospital trust to set up a surveillance process for CRBSI across all specialties of the trust and to reduce CRBSI.
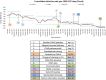
Method: Using a locally adapted CRBSI criteria and root cause analysis (RCA) for investigation we identified a number of opportunities for a quality improvement programme.
Findings: Over a 5-year period we saw a significant and sustained reduction in the rate of CRBSI from 5 per 1000 catheter days to 0.23 per 1000 catheter days.
Conclusions: The surveillance enabled rates of CRBSI to be monitored across the trust and the success of our improvements to be measured.
Keywords: CLABSI; CRBSI; Catheter-related blood stream infections; central line-associated blood stream infections; line surveillance; quality improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology. (2009) Guide to the Elimination of Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections. Washington, DC: APIC; Available at: http://www.apic.org/Resource_/EliminationGuideForm/259c0594–17b0–459d-b3... (last accessed 29th January 2017).
-
- Bion J, Richardson A, Hibbert P, Beer J, Abrusci T, McCutcheon M, Cassidy J, Eddleston J, Gunning K, Bellingan Patten M, Harrison D. (2013) ‘Matching Michigan’: a 2-year stepped interventional programme to minimise central venous catheter-blood stream infections in intensive care units in England. BMJ Quality & Safety 22: 110–123. - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. (2016) Point prevalence survey of healthcare- associated infections and antimicrobial use in European acute care hospitals – protocol version 5.3. Solna: ECDC; Available at: https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/media/en/publications/Publicat... (last accessed 11th November 2017).
-
- Fronzo C. (2017) Approaches for standardising best practice to reduce CRBSI and CLBSI. British Journal of Nursing 26: 19 S32–35. - PubMed
-
- Gorski L, Hadaway L, Hagle M, McGoldrick, Orr M, Doellman D. (2016) Infusion therapy standards of practice. Journal of Infusion Nursing 39 (1S): S1–S159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources