Polydatin prevents fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition through increasing miR-200a to regulate Keap1/Nrf2 pathway
- PMID: 30014902
- PMCID: PMC6068203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.002
Polydatin prevents fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition through increasing miR-200a to regulate Keap1/Nrf2 pathway
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Polydatin prevents fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition through increasing miR-200a to regulate Keap1/Nrf2 pathway" [Redox Biol. 18 (2018) 124-137].Redox Biol. 2019 Apr;22:101101. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101101. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30655077 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
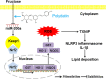
Oxidative stress is a critical factor in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis. MicroRNA-200a (miR-200a) is reported to target Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), which regulates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) anti-oxidant pathway. Polydatin (3,4',5-trihydroxy-stilbene-3-β-D-glucoside), a polyphenol found in the rhizome of Polygonum cuspidatum, have anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperlipidemic effects. However, whether miR-200a controls Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition and the blockade of polydatin are still not clear. Here, we detected miR-200a down-regulation, Keap1 up-regulation, Nrf2 antioxidant pathway inactivation, ROS-driven thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) over-expression, NOD-like receptor (NLR) family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation and dysregulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α (PPAR-α), carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT-1), sterol regulatory element binging protein 1 (SREBP-1) and stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD-1) in rat livers, BRL-3A and HepG2 cells under high fructose induction. Furthermore, the data from the treatment or transfection of miR-200a minic, Keap1 and TXNIP siRNA, Nrf2 activator and ROS inhibitor demonstrated that fructose-induced miR-200a low-expression increased Keap1 to block Nrf2 antioxidant pathway, and then enhanced ROS-driven TXNIP to activate NLRP3 inflammasome and disturb lipid metabolism-related proteins, causing inflammation and lipid deposition in BRL-3A cells. We also found that polydatin up-regulated miR-200a to inhibit Keap1 and activate Nrf2 antioxidant pathway, resulting in attenuation of these disturbances in these animal and cell models. These findings provide a novel pathological mechanism of fructose-induced redox status imbalance and suggest that the enhancement of miR-200a to control Keap1/Nrf2 pathway by polydatin is a therapeutic strategy for fructose-associated liver inflammation and lipid deposition.
Keywords: Excess fructose intake; Keap1/Nrf2 pathway; Liver inflammation and lipid deposition; MiR-200a; Oxidative stress; Polydatin.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Vos M.B., Lavine J.E. Dietary fructose in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2013;57:2525–2531. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Zhang J.H., Chen X.Y., Hu Q.H., Wang M.X., Jin R., Zhang Q.Y., Wang W., Wang R., Kang L.L., Li J.S., Li M., Pan Y., Huang J.J., Kong L.D. Reactive oxygen species-induced TXNIP drives fructose-mediated hepatic inflammation and lipid accumulation through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015;22:848–870. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spahis S., Delvin E., Borys J.M., Levy E. Oxidative stress as a critical factor in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017;26:519–541. - PubMed
-
- Sabouny R., Fraunberger E., Geoffrion M., Ng A.C., Baird S.D., Screaton R.A., Milne R., McBride H.M., Shutt T.E. The Keap1-Nrf2 stress response pathway promotes mitochondrial hyperfusion through degradation of the mitochondrial fission protein Drp1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017;27:1447–1459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

