Systemic inflammation in acute cardiorenal syndrome: an observational pilot study
- PMID: 30015388
- PMCID: PMC6165938
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12327
Systemic inflammation in acute cardiorenal syndrome: an observational pilot study
Abstract
Aims: Acute cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) with and without consideration of the volume state was assessed with regard to inflammatory parameters.
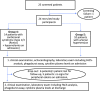
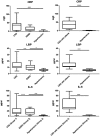
Methods and results: Blood samples from patients with acute CRS (Ronco type 1 or 3, Group 1, n = 15), end-stage renal disease (Group 2, n = 12), hypertension (Group 3, n = 15), and, in a second cohort, with acute CRS and hypervolemia (Group 4, n = 9) and hypertension (Group 5, n = 10) were analysed with regard to lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), interleukins (ILs), and monocyte function (flow cytometry) both on admission (all groups) and on discharge (Groups 1 and 4). By discharge, one Group 1 patient died. LBP (ANOVA for Groups 1-3: P = 0.001) and IL-6 (Kruskal-Wallis for Groups 1-3: P < 0.0001) were higher in Group 1 (LBP: 11.7 ± 2.0 μg/mL; IL-6: 15.0 ± 6.1 pg/mL) and in Group 2 (LBP: 10.4 ± 1.4 μg/mL; IL-6: 14.6 ± 3.8 pg/mL) than in Group 3 (LBP: 5.8 ± 0.4 μg/mL; IL-6: 1.8 ± 0.4 pg/mL). In a direct comparison, the proportion of activated monocytes (CD14 and CD16 positive) was higher in Group 1 (6.9% ± 0.7%) vs. Group 3 (5.1% ± 0.6%; P = 0.018). Group 4 patients had higher IL-6 plasma levels (34.2 ± 10.1 pg/mL) than Group 1 patients (15.0 ± 6.1 pg/mL; P = 0.03). All other findings obtained in CRS groups (Groups 1 and 4) were comparable.
Conclusions: In acute CRS, a state of systemic inflammation was found, which is comparable with the end-stage renal disease situation. In comparison with hypertensive controls, a monocytic activation was found in acute CRS regardless of volume state.
Keywords: Cardiorenal syndrome; Heart failure; Inflammation; Monocyte function.
© 2018 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


References
-
- Ronco C, McCullough P, Anker SD, Anand I, Aspromonte N, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Berl T, Bobek I, Cruz DN, Daliento L, Davenport A, Haapio M, Hillege H, House AA, Katz N, Maisel A, Mankad S, Zanco P, Mebazaa A, Palazzuoli A, Ronco F, Shaw A, Sheinfeld G, Soni S, Vescovo G, Zamperetti N, Ponikowski P. Cardio‐renal syndromes: report from the consensus conference of the acute dialysis quality initiative. Eur Heart J 2010; 31: 703–711. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Athwani V, Bhargava M, Chanchlani R, Mehta AJ. Incidence and outcome of acute cardiorenal syndrome in hospitalized children. Indian J Pediatr 2017; 84: 420–424. - PubMed
-
- Lassus JP, Nieminen MS, Peuhkurinen K, Pulkki K, Siirila‐Waris K, Sund R, Harjola VP. Markers of renal function and acute kidney injury in acute heart failure: definitions and impact on outcomes of the cardiorenal syndrome. Eur Heart J 2010; 31: 2791–2798. - PubMed
-
- Braam B, Joles JA, Danishwar AH, Gaillard CA. Cardiorenal syndrome–current understanding and future perspectives. Nat Rev Nephrol 2014; 10: 48–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

