Probable Locally Acquired Babesia divergens-Like Infection in Woman, Michigan, USA
- PMID: 30016254
- PMCID: PMC6056127
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2408.180309
Probable Locally Acquired Babesia divergens-Like Infection in Woman, Michigan, USA
Abstract
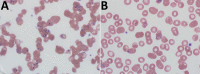
We report an asplenic patient who was infected with Babesia divergens-like/MO-1. The clinical course was complicated by multiorgan failure that required intubation and dialysis. The patient recovered after an exchange transfusion and antimicrobial drug therapy. Physicians should be alert for additional cases, particularly in asplenic persons.
Keywords: B. divergens–like/MO-1; Babesia divergens; Michigan; United States; asplenic patient; babesiosis; emerging infection; erythrocyte exchange transfusion; parasitemia; parasites; protozoa; tickborne disease; ticks; vector-borne infections.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance for babesiosis—United States, 2014. Annual summary [cited 2018 May 19]. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/babesiosis/resources/babesiosis_surveillan...
-
- Wormser GP, Dattwyler RJ, Shapiro ED, Halperin JJ, Steere AC, Klempner MS, et al. The clinical assessment, treatment, and prevention of lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:1089–134. 10.1086/508667 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources