Relative Patlak plot for dynamic PET parametric imaging without the need for early-time input function
- PMID: 30020080
- PMCID: PMC6133657
- DOI: 10.1088/1361-6560/aad444
Relative Patlak plot for dynamic PET parametric imaging without the need for early-time input function
Abstract
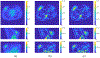
The Patlak graphical method is widely used in parametric imaging for modeling irreversible radiotracer kinetics in dynamic PET. The net influx rate of radiotracer can be determined from the slope of the Patlak plot. The implementation of the standard Patlak method requires the knowledge of full-time input function from the injection time until the scan end time, which presents a challenge for use in the clinic. This paper proposes a new relative Patlak plot method that does not require early-time input function and therefore can be more efficient for parametric imaging. Theoretical analysis proves that the effect of early-time input function is a constant scaling factor on the Patlak slope estimation. Thus, the parametric image of the slope of the relative Patlak plot is related to the parametric image of standard Patlak slope by a global scaling factor. This theoretical finding has been further demonstrated by computer simulation and real patient data. The study indicates that parametric imaging of the relative Patlak slope can be used as a substitute of parametric imaging of standard Patlak slope for tasks that do not require absolute quantification, such as lesion detection and tumor volume segmentation.
Figures
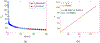
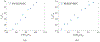
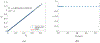
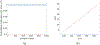
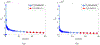
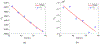
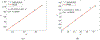
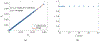

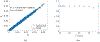

References
-
- Angelis GI, Thielemans K, Tziortzi AC, Turkheimer FE, and Tsoumpas C (2011). Convergence optimization of parametric mlem reconstruction for estimation of patlak plot parameters. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 35(5):407–416. - PubMed
-
- Choi Y, Hawkins RA, Huang SC, Gambhir SS, Brunken RC, Phelps ME, and Schelbert HR (1991). Parametric images of myocardial metabolic-rate of glucose generated from dynamic cardiac pet and 2- f-18 fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose studies. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 32(4):733–738. - PubMed
-
- Choi Y, Huang SC, Hawkins RA, Kuhle WG, Dahlbom M, Hoh CK, Czernin J, Phelps ME, and Schelbert HR (1993). A simplified method for quantification of myocardial blood-flow using nitrogen-13-ammonia and dynamic pet. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 34(3):488–497. - PubMed
-
- Feng D, Huang SC, and Wang XM (1993). Models for computer-simulation studies of input functions for tracer kinetic modeling with positron emission tomography. International Journal of Bio-Medical Computing, 32(2):95–110. - PubMed
-
- Gambhir SS, Schwaiger M, Huang SC, Krivokapich J, Schelbert HR, Nienaber CA, and Phelps ME (1989). Simple noninvasive quantification method for measuring myocardial glucose-utilization in humans employing positron emission tomography and f-18 deoxyglucose. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 30(3):359–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
