The Cow Milk Symptom Score (CoMiSSTM) in presumed healthy infants
- PMID: 30020980
- PMCID: PMC6051613
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200603
The Cow Milk Symptom Score (CoMiSSTM) in presumed healthy infants
Abstract
Objective: The Cow's Milk-related Symptom Score (CoMiSSTM) was developed as an awareness tool to recognize possible manifestations of cow's milk protein allergy (CMPA). Arbitrarily, a cut-off value of ≥12 was defined as a "positive score." The aim of this study was to determine an age-related CoMiSS in healthy infants to minimize the risk of false reassurance or over-diagnosis of CMPA in case of a negative or positive score, respectively.
Methods: General pediatricians determined the CoMiSS in presumed healthy infants aged ≤6 months during a routine visit. Exclusion criteria included any known acute or chronic disease, preterm delivery (< 37 weeks), therapeutic formula, any food supplement (except vitamins) or medication.
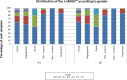
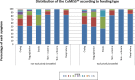
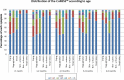
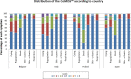
Results: Data from 891 consecutive infants were collected. Complete information was obtained from only 413 (46.4%) infants: Belgium: 31.2%, Italy 18.2%, Poland 19.1% and Spain 31.5%. Since gender (girls vs boys) (p = 0.579) had no influence on the CoMiSS, the data were re-calculated to include those infants with missing gender. The overall median and mean (SD) CoMiSS scores were, respectively, 3.0 and 3.7 (2.9). The 95th percentile was 9. Median crying (p<0.001), regurgitation (p = 0.009) and eczema (p = 0.039) scores differed significantly across the age categories. The other components of the CoMiSS were not age dependent.
Conclusion: In healthy infants ≤ 6 months, the median CoMiSS is 3.0. More prospective studies in different sites and comparing healthy and allergic infants are warranted to obtain further evidence on the utility of the CoMiSS.
Conflict of interest statement
Y. Vandenplas has participated as a clinical investigator, and/or advisory board member, and/or consultant, and/or speaker for Abbott Nutrition, Biocodex, Danone, Nestle Health Science, Nestle Nutrition Institute, Nutricia, Mead Johnson, Phacobel, United Pharmaceuticals. S. Salvatore has participated as a consultant and/or speaker for Danone-Nutricia, Deca, IMS-Health, Menarini, Nestle. Carmen Ribes-Koninckx has participated as a consultant and/or speaker for Danone-Nutricia, Mead-Johnson, Nestle Nutrition Institute. Hania Szajewska had academic-associated speaking engagements and/or received research funding from companies manufacturing infant formulae. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources