Discovery and validation of autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease mutations
- PMID: 30021643
- PMCID: PMC6052673
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-018-0392-9
Discovery and validation of autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease mutations
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that is clinically characterized by progressive cognitive decline. Mutations in amyloid-β precursor protein (APP), presenilin 1 (PSEN1), and presenilin 2 (PSEN2) are the pathogenic cause of autosomal dominant AD (ADAD). However, polymorphisms also exist within these genes.
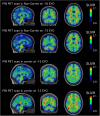
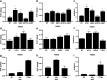
Methods: In order to distinguish polymorphisms from pathogenic mutations, the DIAN Expanded Registry has implemented an algorithm for determining ADAD pathogenicity using available information from multiple domains, including genetic, bioinformatic, clinical, imaging, and biofluid measures and in vitro analyses.
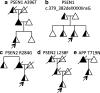
Results: We propose that PSEN1 M84V, PSEN1 A396T, PSEN2 R284G, and APP T719N are likely pathogenic mutations, whereas PSEN1 c.379_382delXXXXinsG and PSEN2 L238F have uncertain pathogenicity.
Conclusions: In defining a subset of these variants as pathogenic, individuals from these families can now be enrolled in observational and clinical trials. This study outlines a critical approach for translating genetic data into meaningful clinical outcomes.
Keywords: APP; Autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease; Cell-based assays; PSEN1; PSEN2; Pathogenicity algorithm.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Washington University Institutional Review Board reviewed the study protocol (IRB no. 201111194). All subjects included in this study, or their proxies, gave written informed consent.
Competing interests
AMG is a member of the scientific advisory board for Denali Therapeutics and serves on a genetic scientific advisory panel for Pfizer. RJB receives laboratory research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Alzheimer’s Association, the BrightFocus Foundation, the Rainwater Foundation Tau Consortium, the Association for Frontotemporal Degeneration, the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund, and the tau SILK Consortium (AbbVie, Biogen, and Eli Lilly and Co.). Funding for clinical trials not related to this research include the National Institutes of Health, the Alzheimer’s Association, Eli Lilly and Co., Hoffman La-Roche, Janssen, Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, the GHR Foundation, and an anonymous foundation. RJB also receives research funding from the DIAN Pharma Consortium (AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Eisai, Eli Lilly and Co., Hoffman La-Roche, Janssen, Pfizer, and Sanofi). RJB has received honoraria from Janssen and Pfizer as a speaker and from Merck and Pfizer as an advisory board member. Washington University, RJB, and DMH have equity ownership interest in C2N Diagnostics and receive royalty income based on technology (stable isotope labeling kinetics and blood plasma assay) licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics. RJB receives income from C2N Diagnostics for serving on the scientific advisory board. Washington University, with RJB as coinventor, has submitted the U.S. nonprovisional patent application “Methods for measuring the metabolism of CNS derived biomolecules in vivo” and the provisional patent application “Plasma based methods for detecting CNS amyloid deposition.” The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Guerreiro RJ, Baquero M, Blesa R, Boada M, Brás JM, Bullido MJ, Calado A, Crook R, Ferreira C, Frank A, et al. Genetic screening of Alzheimer’s disease genes in Iberian and African samples yields novel mutations in presenilins and APP. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:725–731. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.06.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

