Engineering Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Clinical Settings
- PMID: 30023013
- PMCID: PMC6029241
- DOI: 10.5772/58841
Engineering Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Clinical Settings
Abstract
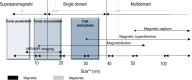
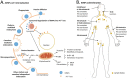
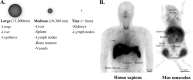
Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) occupy a privileged position among magnetic nanomaterials with potential applications in medicine and biology. They have been widely used in preclinical experiments for imaging contrast enhancement, magnetic resonance, immunoassays, cell tracking, tissue repair, magnetic hyperthermia and drug delivery. Despite these promising results, their successful translation into a clinical setting is strongly dependent upon their physicochemical properties, toxicity and functionalization possibilities. Currently, IONPs-based medical applications are limited to the use of non-functionalized IONPs smaller than 100 nm, with overall narrow particle size distribution, so that the particles have uniform physical and chemical properties. However, the main entry of IONPs into the scene of medical application will surely arise from their functionalization possibilities that will provide them with the capacity to target specific cells within the body, and hence to play a role in the development of specific therapies. In this review, we offer an overview of their basic physicochemical design parameters, giving an account of the progress made in their functionalization and current clinical applications. We place special emphasis on past and present clinical trials.
Keywords: Drug Delivery; IONP; Iron Oxide Nanoparticles; MRI; Magnetic Hyperthermia; Nanomedicine; SPION; USPION; VSPION.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare. No part of this study was performed on any human or animal subject.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (IONP) Synthesis to Applications: Present and Future.Materials (Basel). 2020 Oct 18;13(20):4644. doi: 10.3390/ma13204644. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33080937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in surface chemistry strategies for the fabrication of functional iron oxide based magnetic nanoparticles.Nanoscale. 2013 Nov 21;5(22):10729-52. doi: 10.1039/c3nr04131j. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Nanoscale. 2013. PMID: 24091568
-
Synthesis, Functionalization, and Biomedical Applications of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs).J Funct Biomater. 2024 Nov 12;15(11):340. doi: 10.3390/jfb15110340. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39590545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface engineering of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by polymer grafting: synthesis progress and biomedical applications.Nanoscale. 2020 Jul 23;12(28):14957-14975. doi: 10.1039/d0nr03346d. Nanoscale. 2020. PMID: 32648868 Review.
-
Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications.Biomaterials. 2005 Jun;26(18):3995-4021. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.012. Biomaterials. 2005. PMID: 15626447 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of iron oxide anoparticles in neuronal tissue engineering.Neural Regen Res. 2015 Feb;10(2):189-91. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.152364. Neural Regen Res. 2015. PMID: 25883609 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pulmonary inhalation for disease treatment: Basic research and clinical translations.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Jan 22;25:100966. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100966. eCollection 2024 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 38318475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles in the clinic.Bioeng Transl Med. 2016 Jun 3;1(1):10-29. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10003. eCollection 2016 Mar. Bioeng Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 29313004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravascular Imaging of Atherosclerosis by Using Engineered Nanoparticles.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;13(3):319. doi: 10.3390/bios13030319. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and activation of an iron oxide immobilized drug-mimicking reporter under conventional and pulsed X-ray irradiation conditions.RSC Adv. 2020 Jan 21;10(6):3366-3370. doi: 10.1039/c9ra09828c. eCollection 2020 Jan 16. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coey JMD. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials. Cambridge University Press; 2010.
-
- Ling D, Hyeon T. Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small [Internet] 9(9–10), 1450–1466 (2013). Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/smll.201202111. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baaziz W, Pichon BP, Fleutot S, et al. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Reproducible tuning of the size and nanosized-dependent composition, defects, and spin canting. J. Phys. Chem. C. 118(7), 3795–3810. Available from: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-84894560846&partnerID.... Accessed on 21 Jan 2014.
-
- He Q, Yuan T, Yan X, et al. One-pot synthesis of size-and morphology-controlled 1-D iron oxide nanochains with manipulated magnetic properties. Chem. Commun. 50(2), 201–203 (2014). Available from: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-84889034764&partnerID.... Accessed on 23 Oct 2013. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
