Editorial based on: "Risk of dementia in adults with congenital heart disease: population-based cohort study"
- PMID: 30023115
- PMCID: PMC6036039
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2018.05.167
Editorial based on: "Risk of dementia in adults with congenital heart disease: population-based cohort study"
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
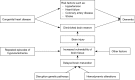
Figures
Comment on
-
Risk of Dementia in Adults With Congenital Heart Disease: Population-Based Cohort Study.Circulation. 2018 May 1;137(18):1912-1920. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029686. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29440121 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources