Electrospun Pectin-Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanofibers for Retinal Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 30023596
- PMCID: PMC6044805
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.7b01604
Electrospun Pectin-Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanofibers for Retinal Tissue Engineering
Abstract
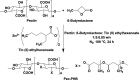
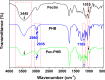
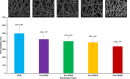
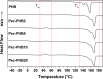
Natural polysaccharide pectin has for the first time been grafted with polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) via ring-opening polymerization of β-butyrolactone. This copolymer, pectin-polyhydroxybutyrate (pec-PHB), was blended with PHB in various proportions and electrospun to produce nanofibers that exhibited uniform and bead-free nanostructures, suggesting the miscibility of PHB and pec-PHB. These nanofiber blends exhibited reduced fiber diameters from 499 to 336-426 nm and water contact angles from 123.8 to 88.2° on incorporation of pec-PHB. They also displayed 39-335% enhancement of elongation at break relative to pristine PHB nanofibers. pec-PHB nanofibers were found to be noncytotoxic and biocompatible. Human retinal pigmented epithelium (ARPE-19) cells were seeded onto pristine PHB and pec-PHB nanofibers as scaffold and showed good proliferation. Higher proportions of pec-PHB (pec-PHB10 and pec-PHB20) yielded higher densities of cells with similar characteristics to normal RPE cells. We propose, therefore, that nanofibers of pec-PHB have significant potential as retinal tissue engineering scaffold materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kai D.; Chua Y. K.; Jiang L.; Owh C.; Chan S. Y.; Loh X. J. Dual functional anti-oxidant and SPF enhancing lignin-based copolymers as additives for personal and healthcare products. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86420–86427. 10.1039/C6RA21433A. - DOI
-
- Kai D.; Ren W.; Tian L.; Chee P. L.; Liu Y.; Ramakrishna S.; Loh X. J. Engineering Poly(lactide)–Lignin Nanofibers with Antioxidant Activity for Biomedical Application. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5268–5276. 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00478. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

