Evaluation of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Inorganic Arsenic Exposure Using Data from Two Diverse Human Populations
- PMID: 30024383
- PMCID: PMC6108830
- DOI: 10.1289/EHP3096
Evaluation of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Inorganic Arsenic Exposure Using Data from Two Diverse Human Populations
Erratum in
-
Erratum: "Evaluation of a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Inorganic Arsenic Exposure Using Data from Two Diverse Human Populations".Environ Health Perspect. 2018 Sep;126(9):99002. doi: 10.1289/EHP4370. Environ Health Perspect. 2018. PMID: 30392381 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Multiple epidemiological studies exist for some of the well-studied health endpoints associated with inorganic arsenic (iAs) exposure; however, results are usually expressed in terms of different exposure/dose metrics. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models may be used to obtain a common exposure metric for application in dose-response meta-analysis.
Objective: A previously published PBPK model for inorganic arsenic (iAs) was evaluated using data sets for arsenic-exposed populations from Bangladesh and the United States.
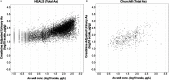
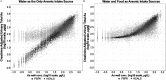
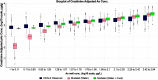
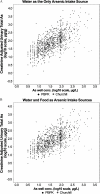
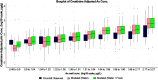
Methods: The first data set was provided by the Health Effects of Arsenic Longitudinal Study cohort in Bangladesh. The second data set was provided by a study conducted in Churchill County, Nevada, USA. The PBPK model consisted of submodels describing the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of iAs and its metabolites monomethylarsenic (MMA) and dimethylarsenic (DMA) acids. The model was used to estimate total arsenic levels in urine in response to oral ingestion of iAs. To compare predictions of the PBPK model against observations, urinary arsenic concentration and creatinine-adjusted urinary arsenic concentration were simulated. As part of the evaluation, both water and dietary intakes of arsenic were estimated and used to generate the associated urine concentrations of the chemical in exposed populations.
Results: When arsenic intake from water alone was considered, the results of the PBPK model underpredicted urinary arsenic concentrations for individuals with low levels of arsenic in drinking water and slightly overpredicted urinary arsenic concentrations in individuals with higher levels of arsenic in drinking water. When population-specific estimates of dietary intakes of iAs were included in exposures, the predictive value of the PBPK model was markedly improved, particularly at lower levels of arsenic intake.
Conclusions: Evaluations of this PBPK model illustrate its adequacy and usefulness for oral exposure reconstructions in human health risk assessment, particularly in individuals who are exposed to relatively low levels of arsenic in water or food. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP3096.
Figures
References
-
- ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). 2007. “Toxicological profile for arsenic (update) [ATSDR Tox Profile]”. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service; http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id=22&tid=3 [accessed 24 May 2018].
-
- Bhattacharya S, Gupta K, Debnath S, Ghosh UC, Chattopadhyay D, Mukhopadhyay A. 2012. Arsenic bioaccumulation in rice and edible plants and subsequent transmission through food chain in Bengal basin: a review of the perspectives for environmental health. Toxicol Environ Chem 94(3):429–441, 10.1080/02772248.2012.657200. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

