Coronary Calcium Score and Cardiovascular Risk
- PMID: 30025580
- PMCID: PMC6056023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.05.027
Coronary Calcium Score and Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
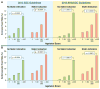
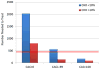
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a highly specific feature of coronary atherosclerosis. On the basis of single-center and multicenter clinical and population-based studies with short-term and long-term outcomes data (up to 15-year follow-up), CAC scoring has emerged as a widely available, consistent, and reproducible means of assessing risk for major cardiovascular outcomes, especially useful in asymptomatic people for planning primary prevention interventions such as statins and aspirin. CAC testing in asymptomatic populations is cost effective across a broad range of baseline risk. This review summarizes evidence concerning CAC, including its pathobiology, modalities for detection, predictive role, use in prediction scoring algorithms, CAC progression, evidence that CAC changes the clinical approach to the patient and patient behavior, novel applications of CAC, future directions in scoring CAC scans, and new CAC guidelines.
Keywords: aspirin; atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; coronary artery calcification; coronary heart disease; statins.
Copyright © 2018 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bild DE, Bluemke DA, Burke GL, et al. Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis: objectives and design. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:871–81. - PubMed
-
- Schmermund A, Möhlenkamp S, Stang A, et al. Heinz Nixdorf RECALL Study Investigative Group. Assessment of clinically silent atherosclerotic disease and established and novel risk factors for predicting myocardial infarction and cardiac death in healthy middle-aged subjects: rationale and design of the Heinz Nixdorf RECALL Study. Am Heart J. 2002;144:212–8. - PubMed
-
- Oei HH, Vliegenthart R, Hak AE, et al. The association between coronary calcification assessed by electron beam computed tomography and measures of extracoronary atherosclerosis: the Rotterdam Coronary Calcification Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:1745–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069771/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

