Long-Term Administration of Tolvaptan in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 30026287
- PMCID: PMC6086720
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01520218
Long-Term Administration of Tolvaptan in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Erratum in
-
Correction.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Jun 7;14(6):910. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02810319. Epub 2019 May 15. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31092536 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and objectives: In the 3-year Tolvaptan Efficacy and Safety in Management of ADPKD and Its Outcomes (TEMPO) 3:4 and 1-year Replicating Evidence of Preserved Renal Function: an Investigation of Tolvaptan Safety and Efficacy in ADPKD (REPRISE) trials, tolvaptan slowed the decline of eGFR in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease at early and later stages of CKD, respectively. Our objective was to ascertain whether the reduction associated with the administration of tolvaptan is sustained, cumulative, and likely to delay the need for kidney replacement therapy.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: One hundred and twenty-eight patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease participated in clinical trials of tolvaptan at the Mayo Clinic. All had the opportunity to enroll into open-label extension studies. Twenty participated in short-term studies or received placebo only. The remaining 108 were analyzed for safety. Ninety seven patients treated with tolvaptan for ≥1 year (mean±SD, 4.6±2.8; range, 1.1-11.2) were analyzed for efficacy using three approaches: (1) comparison of eGFR slopes and outcome (33% reduction from baseline eGFR) to controls matched by sex, age, and baseline eGFR; (2) Stability of eGFR slopes with duration of follow-up; and (3) comparison of observed and predicted eGFRs at last follow-up.
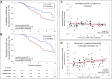
Results: Patients treated with tolvaptan had lower eGFR slopes from baseline (mean±SD, -2.20±2.18 ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year) and from month 1 (mean±SD, -1.97±2.44 ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year) compared with controls (mean±SD, -3.50±2.09 ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year; P<0.001), and lower risk of a 33% reduction in eGFR (risk ratio, 0.63; 95% confidence interval, 0.38 to 0.98 from baseline; risk ratio, 0.53; 95% confidence interval, 0.31 to 0.85 from month 1). Annualized eGFR slopes of patients treated with tolvaptan did not change during follow-up and differences between observed and predicted eGFRs at last follow-up increased with duration of treatment.
Conclusions: Follow-up for up to 11.2 years (average 4.6 years) showed a sustained reduction in the annual rate of eGFR decline in patients treated with tolvaptan compared with controls and an increasing separation of eGFR values over time between the two groups.
Keywords: ADPKD; Benzazepines; EGFR protein, human; Follow-Up Studies; Humans; Polycystic Kidney, Autosomal Dominant; Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor; Renal Insufficiency, Chronic; Renal Replacement Therapy; TEMPO; Tolvaptan; Vasopressin Receptor Antagonist; chronic kidney disease; glomerular filtration rate; polycystic kidney disease; vasopressin.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Ong AC, Devuyst O, Knebelmann B, Walz G; ERA-EDTA Working Group for Inherited Kidney Diseases : Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: The changing face of clinical management. Lancet 385: 1993–2002, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Chapman AB, Devuyst O, Eckardt KU, Gansevoort RT, Harris T, Horie S, Kasiske BL, Odland D, Pei Y, Perrone RD, Pirson Y, Schrier RW, Torra R, Torres VE, Watnick T, Wheeler DC; Conference Participants : Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): Executive summary from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int 88: 17–27, 2015 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Renal Data System US : USRDS 2013 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2013
-
- Belibi FA, Reif G, Wallace DP, Yamaguchi T, Olsen L, Li H, Helmkamp GM Jr ., Grantham JJ: Cyclic AMP promotes growth and secretion in human polycystic kidney epithelial cells. Kidney Int 66: 964–973, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

