Impaired neural stem cell expansion and hypersensitivity to epileptic seizures in mice lacking the EGFR in the brain
- PMID: 30028091
- PMCID: PMC6174950
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14603
Impaired neural stem cell expansion and hypersensitivity to epileptic seizures in mice lacking the EGFR in the brain
Abstract
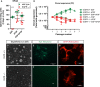
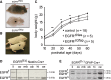
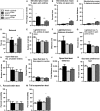
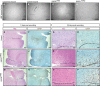
Mice lacking the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) develop an early postnatal degeneration of the frontal cortex and olfactory bulbs and show increased cortical astrocyte apoptosis. The poor health and early lethality of EGFR-/- mice prevented the analysis of mechanisms responsible for the neurodegeneration and function of the EGFR in the adult brain. Here, we show that postnatal EGFR-deficient neural stem cells are impaired in their self-renewal potential and lack clonal expansion capacity in vitro. Mice lacking the EGFR in the brain (EGFRΔbrain ) show low penetrance of cortical degeneration compared to EGFR-/- mice despite genetic recombination of the conditional allele. Adult EGFRΔ mice establish a proper blood-brain barrier and perform reactive astrogliosis in response to mechanical and infectious brain injury, but are more sensitive to Kainic acid-induced epileptic seizures. EGFR-deficient cortical astrocytes, but not midbrain astrocytes, have reduced expression of glutamate transporters Glt1 and Glast, and show reduced glutamate uptake in vitro, illustrating an excitotoxic mechanism to explain the hypersensitivity to Kainic acid and region-specific neurodegeneration observed in EGFR-deficient brains.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; epilepsy; glutamate transporter; neural stem cells; neurodegeneration.
© 2018 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures






References
-
- Sibilia M, Kroismayr R, Lichtenberger BM, Natarajan A, Hecking M & Holcmann M (2007) The epidermal growth factor receptor: from development to tumorigenesis. Differentiation 75, 770–787. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y & Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2, 127–137. - PubMed
-
- Caric D, Raphael H, Viti J, Feathers A, Wancio D & Lillien L (2001) EGFRs mediate chemotactic migration in the developing telencephalon. Development 128, 4203–4216. - PubMed
-
- Kornblum HI, Hussain RJ, Bronstein JM, Gall CM, Lee DC & Seroogy KB (1997) Prenatal ontogeny of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligand, transforming growth factor alpha, in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 380, 243–261. - PubMed
-
- Lillien L & Raphael H (2000) BMP and FGF regulate the development of EGF‐responsive neural progenitor cells. Development 127, 4993–5005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

