Rationale and design of the Virginia Commonwealth University-Anakinra Remodeling Trial-3 (VCU-ART3): A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter study
- PMID: 30033595
- PMCID: PMC6153042
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.22988
Rationale and design of the Virginia Commonwealth University-Anakinra Remodeling Trial-3 (VCU-ART3): A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multicenter study
Abstract
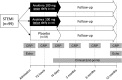
There is clear association between the intensity of the acute inflammatory response during acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and adverse prognosis after AMI. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine released during AMI and involved in adverse remodeling and heart failure (HF). We describe a study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of IL-1 blockade using an IL-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) during the acute phase of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The Virginia Commonwealth University-Anakinra Remodeling Trial-3 (VCU-ART3; http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01950299) is a phase 2, multicenter, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial comparing anakinra 100 mg once or twice daily vs matching placebo (1:1:1) for 14 days in 99 patients with STEMI. Patients who present to the hospital with STEMI within 12 hours of symptom onset will be eligible for enrollment. Patients will be excluded for a history of HF (functional class III-IV), severe valvular disease, severe kidney disease (stage 4-5), active infection, recent use of immunosuppressive drugs, active malignancy, or chronic autoimmune/auto-inflammatory diseases. We will measure the difference in the area under the curve for C-reactive protein between admission and day 14, separately comparing each of the anakinra groups with the placebo group. The P value will be considered significant if <0.025 to adjust for multiple comparisons. Patients will also be followed for up to 12 months from enrollment to evaluate cardiac remodeling (echocardiography), cardiac function (echocardiography), and major adverse cardiovascular outcomes (cardiovascular death, MI, revascularization, and new onset of HF).
Keywords: Interleukin-1; STEMI; study design.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Abbate and Dr. Van Tassell have served as consultants to Swedish Orphan Biovitrum. The authors declare no other potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roubille F, Samri A, Cornillet L, et al. Routinely‐feasible multiple biomarkers score to predict prognosis after revascularized STEMI. Eur J Intern Med. 2010;21:131–136. - PubMed
-
- Seropian IM, Toldo S, Van Tassell BW, et al. Anti‐inflammatory strategies for ventricular remodeling following ST‐segment elevation acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:1593–1603. - PubMed
-
- Abbate A, Van Tassell BW, Biondi‐Zoccai GG. Blocking interleukin‐1 as a novel therapeutic strategy for secondary prevention of cardiovascular events. BioDrugs. 2012;26:217–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous