Phylogeny of Mental Glands, Revisited
- PMID: 30034038
- PMCID: PMC6054469
- DOI: 10.1643/CH-14-210
Phylogeny of Mental Glands, Revisited
Abstract
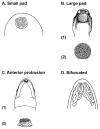
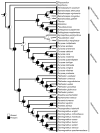
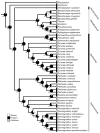
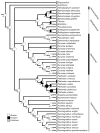
Mental glands and their associated delivery behaviors during courtship are unique to the plethodontid salamanders. Because previous interpretations of the evolution of these features were conducted using older phylogenetic hypotheses, we reanalyzed these traits with newer courtship descriptions and contemporary phylogenetic methods. Using Bayesian ancestral state reconstruction methods that have been developed since the first phylogenetic analyses were conducted in the mid-1990s, we reconstructed mental gland and courtship behavior evolution on a Bayesian phylogeny of the nuclear gene Rag1. The most probable ancestral condition for plethodontids was resolved as presence of a mental gland. Loss of a mental gland occurred in each subfamily and was recovered as the most probable ancestral condition for the Spelerpinae. In contrast, parsimony reconstruction recovered the presence of a mental gland in the ancestor to Spelerpinae with multiple secondary losses. We hypothesize that that absence of a mental gland is possibly ancestral in some clades (i.e., Spelerpinae) and secondary in others (e.g., paedomorphic Eurycea). The most probable ancestral form of the mental gland is likely to be the large pad-type distributed extensively in Plethodontinae and Bolitoglossinae. Desmognathans have the most unique mental glands, occurring in an anterior protrusion or bifurcated form (in Desmognathus wrighti). Fan-shaped mental glands evolved independently in Eurycea and Oedipina. Small pads arose independently in Bolitoglossinae, Plethodontinae, and Spelerpinae. Head-rubbing behavior for mental gland delivery mode was recovered as the most probable and parsimonious ancestral state for the Plethodontidae, with independent losses of this behavior in Plethodontinae and Spelerpinae. Because head-rubbing was observed in outgroups, we hypothesize that head-rubbing behavior predated mental gland evolution. Pulling, snapping, slapping, and biting behaviors evolved independently in the Plethodontinae and Spelerpinae and are not homologous with head-rubbing. All hypotheses of mental gland and courtship evolution invoke homoplasy.
Figures





References
-
- Arnold SJ. Sexual behavior, sexual interference, and sexual defense in the salamanders Ambystoma maculatum, Ambystoma tigrinum and Plethodon jordani. Zeitschrift für Tierpsychologie. 1976;42:247–300.
-
- Beachy CK. Age at maturation, body size, and life-history evolution in the salamander family Plethodontidae. Herpetological Review. 1995;26:179–181.
-
- Beachy CK. Reduced courtship success between parapatric populations of the plethodontid salamander Gyrinophilus porphyriticus. Copeia. 1996;1996:199–203.
-
- Beachy CK. Courtship behavior in the plethodontid salamander Gyrinophilus porphyriticus. Herpetologica. 1997;53:289–296.
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
