Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review
- PMID: 30034873
- PMCID: PMC6052663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.03.005
Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review
Abstract
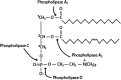
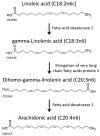
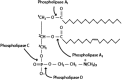
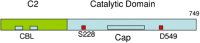
Arachidonic acid (AA), a 20 carbon chain polyunsaturated fatty acid with 4 double bonds, is an integral constituent of biological cell membrane, conferring it with fluidity and flexibility. The four double bonds of AA predispose it to oxygenation that leads to a plethora of metabolites of considerable importance for the proper function of the immune system, promotion of allergies and inflammation, resolving of inflammation, mood, and appetite. The present review presents an illustrated synopsis of AA metabolism, corroborating the instrumental importance of AA derivatives for health and well-being. It provides a comprehensive outline on AA metabolic pathways, enzymes and signaling cascades, in order to develop new perspectives in disease treatment and diagnosis.
Keywords: Arachidonic acid; Delta desaturases; Eicosanoids; Endocannabinoids; Isoprostanes; Lipo- and cyclo-oxygenases.
Figures



References
-
- Rich M.R. Conformational analysis of arachidonic and related fatty acids using molecular dynamics simulations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1178(1):87–96. - PubMed
-
- Taber L., Chiu C.H., Whelan J. Assessment of the arachidonic acid content in foods commonly consumed in the American diet. Lipids. 1998;33(12):1151–1157. - PubMed
-
- Sinclair A.J., Johnson L., O’Dea K., Holman R.T. Diets rich in lean beef increase arachidonic acid and long-chain ω3 polyunsaturated fatty acid levels in plasma phospholipids. Lipids. 1994;29(5):337–343. - PubMed
-
- Li D., Ng A., Mann N.J., Sinclair A.J. Contribution of meat fat to dietary arachidonic acid. Lipids. 1998;33(4):437–440. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

