Survival Outcomes by TP53 Mutation Status in Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 30035249
- PMCID: PMC6050977
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.17.00245
Survival Outcomes by TP53 Mutation Status in Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: We sought to determine the significant genomic alterations in patients with metastatic breast cancer (MBC), and survival outcomes in common genotypes.
Patients and methods: High-depth next generation sequencing was performed for 202 genes in tumor and normal DNA from 257 patients with MBC, including 165 patients with ER/PR+ HER2- (hormone receptor positive, HR+ positive), 32 patients with HER2+ and 60 patients with triple negative (ER/PR/HER2-) cancer. Kaplan Meier survival analysis was performed in our discovery set, in breast cancer patients analyzed in The Cancer Genome Atlas, and in a separate cohort of 98 patients with MBC who underwent clinical genomic testing.
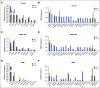
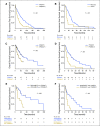
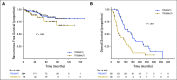
Results: Significantly mutated genes (SMGs) varied by histology and tumor subtype, but TP53 was a SMG in all three subtypes. The most SMGs in HR+ patients included PIK3CA (32%), TP53 (29%), GATA3 (15%), CDH1 (8%), MAP3K1 (8%), PTEN (5%), TGFBR2 (4%), AKT1 (4%), and MAP2K4 (4%). TP53 mutations were associated with shorter recurrence-free survival (P=0.004), progression-free survival (P=0.00057) and overall survival (P=0.003). Further, TP53 status was prognostic among HR+ patients with PIK3CA mutations. TP53 mutations were also associated with poorer overall survival in the 442 HR+ breast cancer patients in the TCGA (P=0.042) and in an independent set of 96 HR+ MBC who underwent clinical sequencing (P=0.0004).
Conclusions: SMGs differ by tumor subtype but TP53 is significantly mutated in all three breast cancer subtypes. TP53 mutations are associated with poor prognosis in HR+ breast cancer. TP53 mutations should be considered in the design and interpretation of precision oncology trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Funda Meric-Bernstam
Xiaofeng Zheng
No relationship to disclose
Maryam Shariati
No relationship to disclose
Senthil Damodaran
No relationship to disclose
Chetna Wathoo
No relationship to disclose
Lauren Brusco
Mehmet Esat Demirhan
No relationship to disclose
Coya Tapia
Agda Karina Eterovic
No relationship to disclose
Reva K. Basho
Naoto T. Ueno
No relationship to disclose
Filip Janku
Aysegul Sahin
No relationship to disclose
Jordi Rodon
Russell Broaddus
No relationship to disclose
Tae-Beom Kim
No relationship to disclose
John Mendelsohn
Kenna R. Mills Shaw
No relationship to disclose
Debu Tripathy
Gordon B. Mills
Ken Chen
No relationship to disclose
Figures

References
-
- Hyman D, Piha-Paul S, Rodón J, et al. : Neratinib for ERBB2 mutant, HER2 non-amplified, metastatic breast cancer: Preliminary analysis from a multicenter, open-label, multi-histology phase II basket trial. Cancer Research 76:PD5, 2016
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

