Multifactorial and multiple component interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community
- PMID: 30035305
- PMCID: PMC6513234
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012221.pub2
Multifactorial and multiple component interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community
Abstract
Background: Falls and fall-related injuries are common, particularly in those aged over 65, with around one-third of older people living in the community falling at least once a year. Falls prevention interventions may comprise single component interventions (e.g. exercise), or involve combinations of two or more different types of intervention (e.g. exercise and medication review). Their delivery can broadly be divided into two main groups: 1) multifactorial interventions where component interventions differ based on individual assessment of risk; or 2) multiple component interventions where the same component interventions are provided to all people.
Objectives: To assess the effects (benefits and harms) of multifactorial interventions and multiple component interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Bone, Joint and Muscle Trauma Group Specialised Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, MEDLINE, Embase, the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, trial registers and reference lists. Date of search: 12 June 2017.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials, individual or cluster, that evaluated the effects of multifactorial and multiple component interventions on falls in older people living in the community, compared with control (i.e. usual care (no change in usual activities) or attention control (social visits)) or exercise as a single intervention.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected studies, assessed risks of bias and extracted data. We calculated the rate ratio (RaR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for rate of falls. For dichotomous outcomes we used risk ratios (RRs) and 95% CIs. For continuous outcomes, we used the standardised mean difference (SMD) with 95% CIs. We pooled data using the random-effects model. We used the GRADE approach to assess the quality of the evidence.
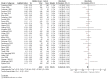
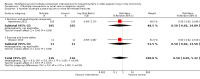
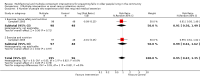
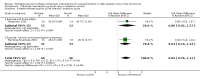
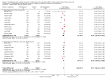
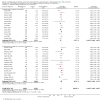
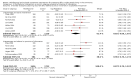
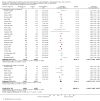
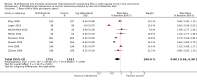
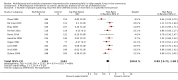
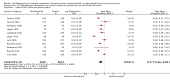
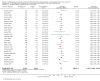
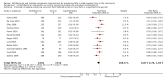
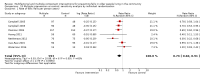
Main results: We included 62 trials involving 19,935 older people living in the community. The median trial size was 248 participants. Most trials included more women than men. The mean ages in trials ranged from 62 to 85 years (median 77 years). Most trials (43 trials) reported follow-up of 12 months or over. We assessed most trials at unclear or high risk of bias in one or more domains.Forty-four trials assessed multifactorial interventions and 18 assessed multiple component interventions. (I2 not reported if = 0%).Multifactorial interventions versus usual care or attention controlThis comparison was made in 43 trials. Commonly-applied or recommended interventions after assessment of each participant's risk profile were exercise, environment or assistive technologies, medication review and psychological interventions. Multifactorial interventions may reduce the rate of falls compared with control: rate ratio (RaR) 0.77, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.87; 19 trials; 5853 participants; I2 = 88%; low-quality evidence. Thus if 1000 people were followed over one year, the number of falls may be 1784 (95% CI 1553 to 2016) after multifactorial intervention versus 2317 after usual care or attention control. There was low-quality evidence of little or no difference in the risks of: falling (i.e. people sustaining one or more fall) (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.03; 29 trials; 9637 participants; I2 = 60%); recurrent falls (RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.03; 12 trials; 3368 participants; I2 = 53%); fall-related hospital admission (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.92 to 1.07; 15 trials; 5227 participants); requiring medical attention (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.10; 8 trials; 3078 participants). There is low-quality evidence that multifactorial interventions may reduce the risk of fall-related fractures (RR 0.73, 95% CI 0.53 to 1.01; 9 trials; 2850 participants) and may slightly improve health-related quality of life but not noticeably (SMD 0.19, 95% CI 0.03 to 0.35; 9 trials; 2373 participants; I2 = 70%). Of three trials reporting on adverse events, one found none, and two reported 12 participants with self-limiting musculoskeletal symptoms in total.Multifactorial interventions versus exerciseVery low-quality evidence from one small trial of 51 recently-discharged orthopaedic patients means that we are uncertain of the effects on rate of falls or risk of falling of multifactorial interventions versus exercise alone. Other fall-related outcomes were not assessed.Multiple component interventions versus usual care or attention controlThe 17 trials that make this comparison usually included exercise and another component, commonly education or home-hazard assessment. There is moderate-quality evidence that multiple interventions probably reduce the rate of falls (RaR 0.74, 95% CI 0.60 to 0.91; 6 trials; 1085 participants; I2 = 45%) and risk of falls (RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.74 to 0.90; 11 trials; 1980 participants). There is low-quality evidence that multiple interventions may reduce the risk of recurrent falls, although a small increase cannot be ruled out (RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.63 to 1.05; 4 trials; 662 participants). Very low-quality evidence means that we are uncertain of the effects of multiple component interventions on the risk of fall-related fractures (2 trials) or fall-related hospital admission (1 trial). There is low-quality evidence that multiple interventions may have little or no effect on the risk of requiring medical attention (RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.67 to 1.35; 1 trial; 291 participants); conversely they may slightly improve health-related quality of life (SMD 0.77, 95% CI 0.16 to 1.39; 4 trials; 391 participants; I2 = 88%). Of seven trials reporting on adverse events, five found none, and six minor adverse events were reported in two.Multiple component interventions versus exerciseThis comparison was tested in five trials. There is low-quality evidence of little or no difference between the two interventions in rate of falls (1 trial) and risk of falling (RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.10; 3 trials; 863 participants) and very low-quality evidence, meaning we are uncertain of the effects on hospital admission (1 trial). One trial reported two cases of minor joint pain. Other falls outcomes were not reported.
Authors' conclusions: Multifactorial interventions may reduce the rate of falls compared with usual care or attention control. However, there may be little or no effect on other fall-related outcomes. Multiple component interventions, usually including exercise, may reduce the rate of falls and risk of falling compared with usual care or attention control.
Conflict of interest statement
SH has no known conflicts of interest. OA is funded on a NIHR Research Methods Programme Systematic Review Fellowship funded by the NIHR (NIHR‐RMFI‐2015‐06‐63).The views expressed in this publication are those of the protocol authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health. BC has no known conflicts of interest. GB has no known conflicts of interest. CS is an author of several trials considered in this review, including an included trial (Fairhall 2014). LC is an author of several trials considered in this review, including an included trial (Clemson 2004). JC is an author of several trials considered in this review, including an included trial (Close 1999). SL is lead author of the ProFaNE consensus for falls guidance and is an author of one of the trials considered in this review.
No review author was involved in study selection or processing of any trials of which they were or are involved.
Figures

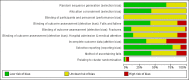

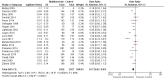









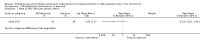

































Comment in
-
Evaluating falls prevention strategies in community settings: marginal reduction on rate of falls with individual risk-based multifactorial interventions compared to 'usual care'.Evid Based Nurs. 2019 Jan;22(1):20. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2018-102995. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Evid Based Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30420489 No abstract available.
-
Are multifactorial and multiple component interventions effective in preventing falls in older people living in the community? A Cochrane Review summary with commentary.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2019 Mar 1;19(1):1-3. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2019. PMID: 30839297 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Beling 2009 {published data only}
-
- Beling J, Roller M. Multifactorial intervention with balance training as a core component among fall‐prone older adults. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy 2009;32(3):125‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Campbell 2005 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs R, Campbell AJ, Robertson MC. Randomized controlled trial of falls prevention in people 75 years and older with severe visual impairment [abstract]. American Academy of Optometry Meeting 2005 Dec 8‐12; San Diego (CA). 2005. [CENTRAL: CN‐00634854]
-
- Kiata L, Kerse NM, Hughes WE, Hayman KJ, Robertson MC, Grow SJ, et al. Agreement and compliance with advice on removing mats or rugs by older people with visual impairments. Journal of Visual Impairment & Blindness 2008;102(3):167‐72.
Carpenter 1990 {published data only}
Carter 1997 {unpublished data only}
-
- Carter S, Campbell E, Sanson‐Fisher R, Tiller K, Gillespie WJ. Trial data (as supplied 1997). Data on file.
Ciaschini 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ciaschini PM, Straus SE, Dolovich LR, Goeree RA, Leung KM, Woods CR, et al. Community‐based intervention to optimise falls risk management: a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2009;38(6):724‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- NCT00465387. FORCE (Falls, Fracture, and Osteoporosis Risk Control Evaluation) study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00465387 (accessed 31 August 2011).
Clemson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Clemson L. Stepping On, reducing falls and building confidence: a practical program that works. Falls prevention in older people: from research to practice. 1st Australian falls prevention conference; 2004 Nov 21‐23; Sydney, Australia. Randwick, NSW, Australia: Prince of Wales Medical Research Institute, 2004:68.
-
- Clemson L, Cumming RG, Kendig H, Swann M, Heard R, Taylor K. The effectiveness of a community‐based program for reducing the incidence of falls in the elderly: a randomized trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2004;52(9):1487‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Clemson L, Taylor K, Kendig H, Cumming RG, Swann M. Recruiting older participants to a randomised trial of a community‐based fall prevention program. Australasian Journal on Ageing 2007;26(1):35‐9. [CINAHL: 2009512824]
-
- Swann M, Clemson L. Evaluating falls efficacy following a community based falls prevention program for older people. Falls prevention in older people: from research to practice. 1st Australian falls prevention conference; 2004 Nov 21‐23; Sydney, Australia. Randwick, NSW, Australia: Prince of Wales Medical Research Institute, 2004:34.
Close 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Close J. Personal communication. 9 December 2008.
-
- Close J, Ellis M, Hooper R, Glucksman E, Jackson S, Swift C. Prevention of falls in the elderly trial (PROFET): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1999;353(9147):93‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Close JC, Ellis M, Hooper R, Glucksman E, Jackson SH, Swift CG. Predictors of falls ‐ results from prevention of falls in the elderly trial (PROFET). Age and Ageing 1999;28(Suppl 1):14.
-
- Close JC, Ellis M, Jackson SH, Glucksman E, Swift CG. Interdisciplinary assessment of elderly people presenting to A&E with a fall [abstract]. Age and Ageing 1998;27(Suppl 1):20.
Coleman 1999 {published data only}
-
- Coleman EA, Grothaus LC, Sandhu N, Wagner EH. Chronic care clinics: a randomized controlled trial of a new model of primary care for frail older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1999;47(7):775‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Davison 2005 {published data only}
-
- Davison J, Bond J, Dawson P, Steen IN, Kenny RA. Patients with recurrent falls attending Accident & Emergency benefit from multifactorial intervention ‐ a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2005;34(2):162‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kenny R. Syncope and Falls in the Emergency Room (SAFER 2) ‐ A multidisciplinary post‐fall assessment and intervention strategy for elderly recurrent fallers attending casualty (RRCC53R). The Research Findings Register. Summary number 1174. www.ReFeR.nhs.uk/ViewRecord.asp?ID=1174 (accessed 24 August 2006).
-
- N0009027144. SAFER2 ‐ Syncope and falls in the emergency room ‐ an explanatory randomised controlled trial of a multidisciplinary post‐fall assessment and intervention strategy in elderly recurrent fallers attending casualty. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 23 February 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0009027144]
-
- N0116069489. Can the incidence of falls in the elderly be reduced by a secondary falls prevention protocol. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 23 February 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0116069489]
-
- N0145036249. A post‐fall intervention strategy after presentation to casualty. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 23 February 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0145036249]
Day 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Fitzharris MP, Day L, Lord SR, Gordon I, Fildes B. The Whitehorse NoFalls trial: effects on fall rates and injurious fall rates. Age & Ageing 2010;39(6):728‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
De Vries 2010 {published data only}
-
- Vries OJ, Peeters GM, Elders PJ, Muller M, Knol DL, Danner SA, et al. Multifactorial intervention to reduce falls in older people at high risk of recurrent falls: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2010;170(13):1110‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- ISRCTN11546541. Prevention of fall incidents in patients with a high risk of falling; a multidisciplinary study on the effects of transmural health care compared to usual care. controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN11546541 (accessed 14 September 2011).
-
- Peeters GM, Vries OJ, Elders PJ, Pluijm SM, Bouter LM, Lips P. Prevention of fall incidents in patients with a high risk of falling: design of a randomised controlled trial with an economic evaluation of the effect of multidisciplinary transmural care. BMC Geriatrics 2007;7:15. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Elley 2008 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12605000054617. Falls Assessment Clinical Trial: randomised controlled trial of a multi‐component intervention in primary health care to reduce falls amongst over 75 year old adults with a history of falling. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=85 (accessed 30 November 2011).
-
- Elley CR, Robertson MC, Garrett S, Kerse NM, MacKinlay E, Lawton B, et al. Effectiveness of a falls‐and‐fracture nurse coordinator to reduce falls: a randomized, controlled trial of at‐risk older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2008;56(8):1383‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fabacher 1994 {published data only}
-
- Fabacher D, Josephson K, Pietruszka F, Linderborn K, Morley JE, Rubenstein LZ. An in‐home preventive assessment program for independent older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1994;42(6):630‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Faes 2011 {published data only}
-
- Faes MC, Reelick MF, Esselink RA, Rikkert MG. Developing and evaluating complex healthcare interventions in geriatrics: the use of the medical research council framework exemplified on a complex fall prevention intervention. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2010;58(11):2212‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Faes MC, Reelick MF, Melis RJ, Borm GF, Esselink RA, Olde Rikkert MG. Multifactorial fall prevention for pairs of frail community‐dwelling older fallers and their informal caregivers: a dead end for complex interventions in the frailest fallers. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2011; Vol. 12, issue 6:451‐8. - PubMed
-
- NCT00512655. Trial to reduce falls incidence rate in frail elderly (CP). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00512655 (accessed 31 August 2011).
-
- Reelick MF, Faes MC, Esselink RA, Kessels RP, Olde Rikkert MG. How to perform a preplanned process evaluation for complex interventions in geriatric medicine: exemplified with the process evaluation of a complex falls‐prevention program for community‐dwelling frail older fallers. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2011;12(5):331‐6. - PubMed
Fairhall 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fairhall N, Sherrington C, Kurrle SE, Lord SR, Lockwood K, Howard K, et al. Economic evaluation of a multifactorial, interdisciplinary intervention versus usual care to reduce frailty in frail older people. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2015;16(1):41‐8. [PUBMED: 25239014] - PubMed
-
- Fairhall N, Sherrington C, Lord SR, Kurrle SE, Langron C, Lockwood K, et al. Effect of a multifactorial, interdisciplinary intervention on risk factors for falls and fall rate in frail older people: a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2014;43(5):616‐22. [PUBMED: 24381025] - PubMed
Ferrer 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ferrer A, Badia T, Formiga F, Almeda J, Fernandez C, Pujol R. Gender differences in health status in a population of over 85 year‐olds. The Octabaix study [Diferencias de genero en el perfil de salud de una cohorte de 85 años. Estudio Octabaix]. Atencion Primaria 2011;43(11):577‐84. [EMBASE: 2011609254] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferrer A, Badia T, Formiga F, Gil A, Padros G, Sarro M, et al. A randomized clinical trial of falls and malnutrition prevention in community‐dwelling elders aged 85 years old. The OCTABAIX study [Ensayo clinico aleatorizado de prevencion de caidas y malnutricion en personas de 85 años en la comunidad. Estudio OCTABAIX]. Revista Espanola de Geriatria y Gerontologia 2010;45(2):79‐85. - PubMed
Freiberger 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Freiberber E. Personal communication. 25 October 2007.
-
- Freiberger E. Personal communication. 12 December 2007.
-
- Freiberger E, Haberle L, Spirduso WW, Zijlstra GA. Long‐term effects of three multicomponent exercise interventions on physical performance and fall‐related psychological outcomes in community‐dwelling older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2012;30(3):437‐46. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03859.x] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Freiberger E, Menz HB. Characteristics of falls in physically active community‐dwelling older people: Findings from the 'Standfest im Alter' study. Zeitschrift fur Gerontologie und Geriatrie 2006;39(4):261‐7. - PubMed
-
- Freiberger E, Menz HB, Abu‐Omar K, Rutten A. Preventing falls in physically active community‐dwelling older people: a comparison of two intervention techniques. Gerontology 2007;53(5):298‐305. - PubMed
Gallagher 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gallagher EM, Brunt H. Head over heels: impact of a health promotion program to reduce falls in the elderly. Canadian Journal on Aging 1996;15(1):84‐96. [EMBASE 1996164172]
Hagovska 2016 {published data only}
-
- Hagovska M, Olekszyova Z. Impact of the combination of cognitive and balance training on gait, fear and risk of falling and quality of life in seniors with mild cognitive impairment. Geriatrics and Gerontology International 2016;16(9):1043‐50. [PUBMED: 26338465] - PubMed
Hendriks 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bleijlevens MH, Hendriks MR, Haastregt JC, Crebolder HF, Eijk JT. Lessons learned from a multidisciplinary fall‐prevention programme: the occupational‐therapy element. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2010;17(4):319‐25. - PubMed
-
- Hendriks MR, Bleijlevens MH, Haastregt JC, Crebolder HF, Diederiks JP, Evers SM, et al. Lack of effectiveness of a multidisciplinary fall‐prevention program in elderly people at risk: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2008;56(8):1390–7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hendriks MR, Bleijlevens MH, Haastregt JC, Bruijn FH, Diederiks JP, Mulder WJ, et al. A multidisciplinary fall prevention program for elderly persons: a feasibility study. Geriatric Nursing 2008;29(3):186‐96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hendriks MR, Evers SM, Bleijlevens MH, Haastregt JC, Crebolder HF, Eijk JT. Cost‐effectiveness of a multidisciplinary fall prevention program in community‐dwelling elderly people: A randomized controlled trial (ISRCTN 64716113). International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2008;24(2):193‐202. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hogan 2001 {published data only}
Huang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Huang TT, Liang SH. A randomized clinical trial of the effectiveness of a discharge planning intervention in hospitalized elders with hip fracture due to falling. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2005;14(10):1193‐201. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Huang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Huang HC, Liu CY, Huang YT, Kernohan WG. Community‐based interventions to reduce falls among older adults in Taiwan ‐ long time follow‐up randomised controlled study. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2010;19(7‐8):959‐68. - PubMed
Huang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Huang TT, Wang WS. Comparison of three established measures of fear of falling in community‐dwelling older adults: psychometric testing. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2009;46(10):1313‐9. - PubMed
-
- Huang TT, Yang LH, Liu CY. Reducing the fear of falling among community‐dwelling elderly adults through cognitive‐behavioural strategies and intense Tai Chi exercise: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2011; Vol. 67, issue 5:961‐71. - PubMed
Imhof 2012 {published data only}
Jitapunkul 1998 {published data only}
-
- Jitapunkul S. A randomised controlled trial of regular surveillance in Thai elderly using a simple questionnaire administered by non‐professional personnel. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1998;81(5):352‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kingston 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kingston P, Jones M, Crome P. A RCT of health visitor (HV) intervention in falls. Age and Ageing 2001;30(Suppl 1):40.
-
- Kingston P, Jones M, Lally F, Crome P. Older people and falls: A randomized controlled trial of a health visitor (HV) intervention. Reviews in Clinical Gerontology 2001;11(3):209‐14. [EMBASE: 2002061828]
-
- Kingston PA. Older People and 'Falls' A Randomised Control Trial of Health Visitor Intervention [thesis]. Stoke‐on‐Trent (UK): Keele University, 1998.
-
- N0498009612. Elderly people and accidents: a prospective analysis of accidental causation among elderly populations and their post discharge requirements. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 23 February 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0498009612]
Lightbody 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lightbody E, Watkins C, Leathley M, Sharma A, Lye M. Evaluation of a nurse‐led falls prevention programme versus usual care: a randomized controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2002;31(3):203‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- N0500000414. Fallers attending casualty. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 23 February 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0500000414]
Logan 2010 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN10538608. Evaluation of the costs and benefits of computerised on‐scene decision support for emergency ambulance personnel to assess and plan appropriate care for older people who have fallen: a randomised controlled trial. controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN10538608 (accessed 23 September 2011).
-
- N0171168738. An evaluation of the Primary Care falls prevention services for older fallers presenting to the ambulance service. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 30 November 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0171168738]
-
- Sach TH, Logan PA, Coupland CA, Gladman JR, Sahota O, Stoner‐Hobbs V, et al. Community falls prevention for people who call an emergency ambulance after a fall: an economic evaluation alongside a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2012; Vol. 41, issue 5:635‐41. [DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afs071] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lord 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lord SR, Tiedemann A, Chapman K, Munro B, Murray SM, Gerontology M, et al. The effect of an individualized fall prevention program on fall risk and falls in older people: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2005;53(8):1296‐304. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Luck 2013 {published data only}
Markle‐Reid 2010 {published data only}
-
- Markle‐Reid M, Browne G, Gafni A, Roberts J, Weir R, Thabane L, et al. The effects and costs of a multifactorial and interdisciplinary team approach to falls prevention for older home care clients 'at risk' for falling: a randomized controlled trial. Canadian Journal of Aging 2010;29(1):139‐61. - PubMed
-
- Markle‐Reid M, Miles M, Vaitonis V, Henderson S, Browne Weir R, et al. From Isolation to Integration: the Effects and Costs of a Multifactorial and Interdisciplinary Team Approach to Falls Prevention for Frail Older Home Care Clients. Final Research Report. Edmonton: Canadian Patient Safety Institute, 2008.
-
- NCT00463658. Interdisciplinary falls prevention for seniors. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00463658 (accessed 31 August 2011).
Mendoza‐Ruvalcaba 2015 {published data only}
Metzelthin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Metzelthin SF, Rossum E, Witte LP, Ambergen AW, Hobma SO, Sipers W, et al. Effectiveness of interdisciplinary primary care approach to reduce disability in community dwelling frail older people: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2013;347:f5264. [PUBMED: 24022033] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Metzelthin SF, Rossum E, Hendriks MR, Witte LP, Hobma SO, Sipers W, et al. Reducing disability in community‐dwelling frail older people: cost‐effectiveness study alongside a cluster randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2015;44(3):390‐6. [PUBMED: 25566783] - PubMed
Möller 2014 {published data only}
-
- Möller UO, Kristensson J, Midlöv P, Ekdahl C, Jakobsson U. Effects of a one‐year home‐based case management intervention on falls in older people: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Aging and Physical Activity 2014;22(4):457‐64. [PUBMED: 24152667] - PubMed
Neelemaat 2012 {published data only}
-
- Neelemaat F, Bosmans JE, Thijs A, Seidell JC, Bokhorst‐de van der Schueren MA. Post‐discharge nutritional support in malnourished elderly individuals improves functional limitations. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2011;12(4):295‐301. - PubMed
-
- Neelemaat F, Lips P, Bosmans JE, Thijs A, Seidell JC, Bokhorst‐de van der Schueren MA. Short‐term oral nutritional intervention with protein and vitamin D decreases falls in malnourished older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2012;60(4):691‐9. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03888.x] - DOI - PubMed
Newbury 2001 {published data only}
-
- Newbury JW, Marley JE, Beilby J. A randomised controlled trial of the outcome of health assessment of people aged 75 years and over. Medical Journal of Australia 2001;175(2):104‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ng 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ng TP, Feng L, Nyunt MS, Feng L, Niti M, Tan BY, et al. Nutritional, physical, cognitive, and combination interventions and frailty reversal among older adults: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Medicine 2015;128(11):1225‐36.e1. [PUBMED: 26159634] - PubMed
Olsen 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bergland A, Thorsen H, Karesen R. Effect of exercise on mobility, balance, and health‐related quality of life in osteoporotic women with a history of vertebral fracture: a randomized, controlled trial. Osteoporosis International 2011;22(6):1863‐71. [PUBMED: 21060992] - PubMed
-
- Olsen CF, Bergland A. The effect of exercise and education on fear of falling in elderly women with osteoporosis and a history of vertebral fracture: results of a randomized controlled trial. Osteoporosis International 2014;25(8):2017‐25. [PUBMED: 24807628] - PubMed
Palvanen 2014 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN48015966. The Chaos Clinic for prevention of falls and related injuries: a randomised, controlled trial. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN48015966 (accessed 2 September 2011).
-
- Palvanen M, Kannus P, Piirtola M, Niemi S, Parkkari J, Jarvinen M. Effectiveness of the Chaos Falls Clinic in preventing falls and injuries of home‐dwelling older adults: a randomised controlled trial. Injury 2014;45(1):265‐71. [PUBMED: 23579066] - PubMed
Pardessus 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pardessus V, Puisieux F, Pompeo C, Gaudefroy C, Thevenon A, Dewailly P. Benefits of home visits for falls and autonomy in the elderly: a randomized trial study. American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2002;81(4):247‐52. [PUBMED: 11953541] - PubMed
Rubenstein 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Alessi C. Personal communication. 10 June 2007.
-
- Josephson K. Personal communication. 20 November 2007.
-
- Rubenstein LZ, Alessi CA, Josephson KR, Trinidad Hoyl M, Harker JO, Pietruszka FM. A randomized trial of a screening, case finding, and referral system for older veterans in primary care. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2007;55(2):166‐74. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Russell 2010 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12605000672651. A randomised controlled trial to reduce further falls and injuries for older fallers presenting to an Emergency Department. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=849 (accessed 14 September 2011).
-
- Hill K, Womer M, Russell M, Blackberry I, McGann A. Fear of falling in older fallers presenting at emergency departments. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2010;66(8):1769‐79. - PubMed
-
- NCT00217360. RCT to reduce further falls and injuries for older fallers presenting to an Emergency Department. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00217360 (accessed 14 September 2011).
-
- Russell MA, Hill KD, Day LM, Blackberry I, Schwartz J, Giummarra MJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a multifactorial falls prevention intervention for older fallers presenting to Emergency Departments. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2010;58:2265–74. - PubMed
Schrijnemaekers 1995 {published data only}
-
- Schrijnemaekers VJ, Haveman MJ. Effects of preventive outpatient geriatric assessment: short‐term results of a randomized controlled study. Home Health Care Services Quarterly 1995;15(2):81‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Serra‐Prat 2017 {published data only}
-
- Serra‐Prat M, Sist X, Domenich R, Jurado L, Saiz A, Roces A, et al. Effectiveness of an intervention to prevent frailty in pre‐frail community‐dwelling older people consulting in primary care: a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2017;46(3):401‐7. [PUBMED: 28064172] - PubMed
Sheffield 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sheffield C, Smith CA, Becker M. Evaluation of an agency‐based occupational therapy intervention to facilitate aging in place. Gerontologist 2013;53(6):907‐18. [PUBMED: 23213082] - PubMed
Shyu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Shyu YI, Liang J, Wu CC, Su JY, Cheng HS, Chou SW, et al. Interdisciplinary intervention for hip fracture in older Taiwanese: benefits last for 1 year. Journals of Gerontology Series A‐Biological Sciences & Medical Sciences 2008;63(1):92‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Shyu YI, Liang J, Wu CC, Su JY, Cheng HS, Chou SW, et al. Two‐year effects of interdisciplinary intervention for hip fracture in older Taiwanese. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2010;58(6):1081‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sosnoff 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sosnoff JJ, Moon Y, Wajda DA, Finlayson ML, McAuley E, Peterson EW, et al. Fall risk and incidence reduction in high risk individuals with multiple sclerosis: a pilot randomized control trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2015;29(10):952‐60. [PUBMED: 25540170] - PubMed
Spice 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- George S, Spice C, Morotti W, Rose J, Harris S, Gordon C. The Winchester Falls Project: a cluster randomised community intervention trial of secondary prevention of falls in community dwelling older people. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2006;60(Suppl 1):A17.
-
- N0278078805. The Winchester Falls Project: A randomised controlled trial of multidisciplinary assessment in the secondary prevention of falls. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 23 February 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0278078805]
-
- NCT00130624. The Winchester Falls Project: A cluster randomised community intervention trial of secondary prevention of falls in community‐dwelling older people. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00130624 (accessed 30 November 2011).
-
- Spice C. Personal communication. 24 December 2006.
-
- Spice C, Morotti W, Dent T, George S, Rose J, Gordon C. The Winchester Falls Project: A randomised controlled trial of secondary falls prevention. Age and Ageing 2005;34(Suppl 2):ii18. - PubMed
Tinetti 1994 {published data only}
-
- King MB, Tinetti ME. A multifactorial approach to reducing injurious falls. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine 1996;12(4):745‐59. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Koch M, Gottschalk M, Baker DI, Palumbo S, Tinetti ME. An impairment and disability assessment and treatment protocol for community‐living elderly persons. Physical Therapy 1994;74:286‐94; discussion 295‐8. - PubMed
-
- Rizzo JA, Baker DI, McAvay G, Tinetti ME. The cost‐effectiveness of a multifactorial targeted prevention program for falls among community elderly persons. Medical Care 1996;34(9):954‐69. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Tinetti ME. Prevention of falls and fall injuries in elderly persons: a research agenda. Preventive Medicine 1994;23(5):756‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Tinetti ME, Baker DI, Garrett PA, Gottschalk M, Koch ML, Horwitz RI. Yale FICSIT: risk factor abatement strategy for fall prevention. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1993;41:315‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ueda 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ueda T, Higuchi Y, Imaoka M, Todo E, Kitagawa T, Ando S. Tailored education program using home floor plans for falls prevention in discharged older patients: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2017;71:9‐13. [PUBMED: 28242580] - PubMed
Uusi‐Rasi 2015 {published data only}
-
- NCT00986466. Vitamin D and exercise in falls prevention (DEX). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00986466 (accessed 31 August 2011).
-
- Patil R, Kolu P, Raitanen J, Valvanne J, Kannus P, Karinkanta S, et al. Cost‐effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation and exercise in preventing injurious falls among older home‐dwelling women: findings from an RCT. Osteoporosis International 2016;27(1):193‐201. [PUBMED: 26205890] - PubMed
-
- Patil R, Uusi‐Rasi K, Tokola K, Karinkanta S, Kannus P, Sievanen H. Effects of a multimodal exercise program on physical function, falls, and injuries in older women: A 2‐year community‐based, randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2015;63(7):1306‐13. [PUBMED: 26115073] - PubMed
-
- Uusi‐Rasi K, Patil R, Karinkanta S, Kannus P, Tokola K, Lamberg‐Allardt C, et al. A 2‐year follow‐up after a 2‐year RCT with vitamin D and exercise: effects on falls, injurious falls and physical functioning among older women. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 2017;72(9):1239‐45. [PUBMED: 28369286] - PMC - PubMed
Van Haastregt 2000 {published data only}
-
- Haastregt JC, Rossum E, Diederiks JP, Witte LP, Voorhoeve PM, Crebolder HF. Process‐evaluation of a home visit programme to prevent falls and mobility impairments among elderly people at risk. Patient Education and Counseling 2002;47(4):301‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Haastregt JC, Rossum E, Diederiks JP, Voorhoeve PM, Witte LP, Crebolder HF. Preventing falls and mobility problems in community‐dwelling elders: the process of creating a new intervention. Geriatric Nursing 2000;21(6):309‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Van Rossum 1993 {published data only}
Vetter 1992 {published data only}
Vind 2009 {published data only}
-
- NCT00226486. Examination and treatment of elderly after a fall. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00226486 (accessed 31 August 2011).
-
- Vind AB. Personal communication. 30 March 2006.
-
- Vind AB, Andersen HE, Pedersen KD, Joergensen T, Schwarz P. Effect of a program of multifactorial fall prevention on health‐related quality of life, functional ability, fear of falling and psychological well‐being. A randomized controlled trial. Aging ‐ Clinical and Experimental Research 2010;22(3):249‐54. - PubMed
-
- Vind AB, Andersen HE, Pedersen KD, Jorgensen T, Schwarz P. An outpatient multifactorial falls prevention intervention does not reduce falls in high‐risk elderly Danes. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2009;57(6):971‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Vind AB, Andersen HE, Pedersen KD, Jorgensen T, Schwarz P. Baseline and follow‐up characteristics of participants and nonparticipants in a randomized clinical trial of multifactorial fall prevention in Denmark. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2009;57(10):1844‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wagner 1994 {published data only}
Waterman 2016 {published data only}
Wesson 2013 {published data only}
Whitehead 2003 {published data only}
-
- Whitehead C, Wundke R, Crotty M, Finucane P. Evidence‐based clinical practice in falls prevention: a randomised controlled trial of a falls prevention service. Australian Health Review 2003;26(3):88‐96. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wilder 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wilder P. Seniors to seniors exercise program: a cost effective way to prevent falls in the frail elderly living at home. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy 2001;24(3):13.
Zijlstra 2009 {published data only}
-
- Haastregt JC, Zijlstra GA, Hendriks MR, Goossens ME, Eijk JT, Kempen GI. Cost‐effectiveness of an intervention to reduce fear of falling. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2013;29(3):219‐26. [PUBMED: 23778198] - PubMed
-
- Zijlstra GA, Haastregt JC, Ambergen T, Rossum E, Eijk JT, Tennstedt SL, et al. Effects of a multicomponent cognitive behavioral group intervention on fear of falling and activity avoidance in community‐dwelling older adults: results of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2009;57(11):2020‐8. [PUBMED: 19793161] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ACTRN12610000838011 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12610000838011. In community‐dwelling older people who have fallen, does the provision of falls prevention interventions and osteoporosis treatment through a specialist Falls and Bone service prevent more falls than care coordinated by General Practitioners. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=335807 (accessed 30 November 2011).
Alexander 2003 {published data only}
-
- Alexander N. Personal communication. 23 August 2006.
-
- Alexander NB, Bentur N, Strasburg D, Nyquist LV. Fall risk reduction in Israeli day care center attendees using exercise and behavior strategies. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(Suppl 4):S117.
Assantachai 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Assantachai P. Personal communication. 11 June 2007.
-
- Assantachai P, Chatthanawaree W, Thamlikitkul V, Praditsuwan R, Pisalsarakij D. Strategy to prevent falls in the Thai elderly: a controlled study integrated health research program for the Thai elderly. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2002;85(2):215‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bruce 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bruce J, Lall R, Withers EJ, Finnegan S, Underwood M, Hulme C, et al. A cluster randomised controlled trial of advice, exercise or multifactorial assessment to prevent falls and fractures in community‐dwelling older adults: protocol for the prevention of falls injury trial (PreFIT). BMJ Open 2016;6(1):e009362. [PUBMED: 26781504] - PMC - PubMed
Chu 2017 {published data only}
-
- Chu MM, Fong KN, Lit AC, Rainer TH, Cheng SW, Au FL, et al. An occupational therapy fall reduction home visit program for community‐dwelling older adults in Hong Kong after an emergency department visit for a fall. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2017;65(2):364‐72. [PUBMED: 27858951] - PubMed
Clemson 2012 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12606000025538. Lifestyle (LIFE) versus structured balance and strength training to reduce falls in the elderly: a randomized trial. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=1007 (accessed 15 June 2012).
-
- Clemson L, Fiatarone Singh MA, Bundy A, Cumming RG, Manollaras K, O'Loughlin P, et al. Integration of balance and strength training into daily life activity to reduce rate of falls in older people (the LiFE study): randomised parallel trial. BMJ 2012; Vol. 345, issue 7870:Article Number: e4547. - PMC - PubMed
Cockayne 2014 {published data only}
Cohen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cohen MA, Miller J, Shi X, Sandhu J, Lipsitz LA. Prevention program lowered the risk of falls and decreased claims for long‐term services among elder participants. Health Affairs 2015;34(6):971‐7. [PUBMED: 26056202] - PubMed
Comans 2010 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12605000056695. Domiciliary versus centre‐based rehabilitation of older community dwellers: Randomised trial with economic evaluation. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=52 (accessed 30 November 2011).
-
- Comans TA, Brauer S, Haines T. Domiciliary vs centre‐based rehabilitation of older community dwellers: randomised trial with economic evaluation. Open Geriatric Medicine Journal 2008;1(6):62‐7.
-
- Comans TA, Brauer SG, Haines TP. Randomized trial of domiciliary versus center‐based rehabilitation: which is more effective in reducing falls and improving quality of life in older fallers?. Journals of Gerontology Series A‐Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 2010;65(6):672‐9. - PubMed
-
- Comans TA, Currin ML, Brauer SG, Haines TP. Factors associated with quality of life and caregiver strain amongst frail older adults referred to a community rehabilitation service: implications for service delivery. Disability and Rehabilitation 2011;33(13‐14):1215‐21. - PubMed
Conroy 2010 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN46584556. Multifactorial day hospital intervention to reduce falls in high risk older people in primary care: a multi‐centre randomised controlled trial. controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN46584556 (accessed 14 September 2011). - PMC - PubMed
De Negreiros 2013 {published data only}
-
- Negreiros Cabral K, Perracini MR, Soares AT, Cristo Stein F, Sera CT, Tiedemann A, et al. Effectiveness of a multifactorial falls prevention program in community‐dwelling older people when compared to usual care: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial (Prevquedas Brazil). BMC Geriatrics 2013;13:27. [PUBMED: 23497000] - PMC - PubMed
Di Monaco 2008 {published data only}
-
- Monaco M, Vallero F, Toma E, Lauso L, Tappero R, Cavanna A. A single home visit by an occupational therapist reduces the risk of falling after hip fracture in elderly women: a quasi‐randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2008;40(6):446‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Fox 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fox PJ, Vazquez L, Tonner C, Stevens JA, Fineman N, Ross LK. A randomized trial of a multifaceted intervention to reduce falls among community‐dwelling adults. Health Education and Behavior 2010;37(6):831‐48. - PubMed
Gianoudis 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gianoudis J, Bailey CA, Ebeling PR, Nowson CA, Sanders KM, Hill K, et al. Effects of a targeted multimodal exercise program incorporating high‐speed power training on falls and fracture risk factors in older adults: a community‐based randomized controlled trial. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2014;29(1):182‐91. [PUBMED: 23775701] - PubMed
Gill 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gill DP, Zou GY, Jones GR, Speechley M. Injurious falls are associated with lower household but higher recreational physical activities in community‐dwelling older male veterans. Gerontology 2008;54(2):106‐15. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Speechley M. Falls data (as supplied 03 June 2008). Data on file.
Giordano 2016 {published data only}
-
- Giordano A, Bonometti GP, Vanoglio F, Paneroni M, Bernocchi P, Comini L, et al. Feasibility and cost‐effectiveness of a multidisciplinary home‐telehealth intervention programme to reduce falls among elderly discharged from hospital: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatrics 2016;16(1):209. [PUBMED: 27923343] - PMC - PubMed
Hill 2000 {published data only}
-
- Crome P. Personal communication. 29 August 2006.
-
- Crome P, Hill S, Mossman J, Stockdale P. A randomised controlled trial of a nurse led falls prevention clinic. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2000;48(8):S78.
-
- Hill S, Mossman J, Stockdale P, Crome P. A randomised controlled trial of a nurse‐led falls prevention clinic. Age and Ageing 2000;29(Suppl 2):20.
Hornbrook 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hornbrook MC, Stevens VJ, Wingfield DJ. Seniors' program for injury control and education. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1993;41(3):309‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hornbrook MC, Stevens VJ, Wingfield DJ, Hollis JF, Greenlick MR, Ory MG. Preventing falls among community‐dwelling older persons: results from a randomized trial. Gerontologist 1994;34(1):16‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Stevens VJ, Hornbrook MC, Wingfield DJ, Hollis JF, Greenlick MR, Ory MG. Design and implementation of a falls prevention intervention for community‐dwelling older persons. Behavior, Health, and Aging 1991/92;2(1):57‐73.
Huang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Huang TT, Acton GJ. Effectiveness of home visit falls prevention strategy for Taiwanese community‐dwelling elders: randomized trial. Public Health Nursing 2004;21(3):247‐56. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lamb 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bruce J, Lall R, Withers EJ, Finnegan S, Underwood M, Hulme C, et al. A cluster randomised controlled trial of advice, exercise or multifactorial assessment to prevent falls and fractures in community‐dwelling older adults: protocol for the prevention of falls injury trial (PreFIT). BMJ Open 2016;6(1):e009362. [PUBMED: 26781504] - PMC - PubMed
-
- ISRCTN71002650. Prevention of Fall Injury Trial: a parallel group cluster randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN71002650 (accessed 22 Sept 2010).
-
- Lamb S. Prevention of fall related injuries trial (Pre‐FIT). www.hta.ac.uk/2146 (accessed 22 Sept 2010).
Lee 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lee HC, Chang KC, Tsauo JY, Hung JW, Huang YC, Lin SI. Effects of a multifactorial fall prevention program on fall incidence and physical function in community‐dwelling older adults with risk of falls. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2013;94(4):606‐15, 615.e1. [PUBMED: 23220343] - PubMed
Mahoney 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mahoney JE, Shea TA, Przybelski R, Jaros L, Gangnon R, Cech S, et al. Kenosha County falls prevention study: a randomized, controlled trial of an intermediate‐intensity, community‐based multifactorial falls intervention. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2007;55(4):489‐98. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Matchar 2017 {published data only}
-
- Matchar DB, Duncan PW, Lien CT, Ong MEH, Lee M, Gao F, et al. Randomized controlled trial of screening, risk modification, and physical therapy to prevent falls among the elderly recently discharged from the emergency department to the community: the steps to avoid falls in the elderly study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2017;98(6):1086‐96. [PUBMED: 28202383] - PubMed
Mikolaizak 2017 {published data only}
-
- Mikolaizak AS, Lord SR, Tiedemann A, Simpson P, Caplan GA, Bendall J, et al. A multidisciplinary intervention to prevent subsequent falls and health service use following fall‐related paramedic care: a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2017;46(2):200‐7. [PUBMED: 28399219] - PubMed
NCT00126152 {published data only}
-
- NCT00126152. Senior Falls Prevention Study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00126152 (accessed 13 June 2017).
NCT00483275 {published data only}
-
- NCT00483275. Fall prevention by alfacalcidol and training (SPALT). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00483275 (accessed 23 February 2011).
Perula 2012 {published data only}
-
- Perula LA, Varas‐Fabra F, Rodriguez V, Ruiz‐Moral R, Fernandez JA, Gonzalez J, et al. Effectiveness of a multifactorial intervention program to reduce falls incidence among community‐living older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2012;93(10):1677‐84. [PUBMED: 22609117] - PubMed
Salminen 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kivela S‐L, Aarnio P, Asikainen E, Hyttinen H, Isoaho R, Karra E, et al. Prevention of injurious falls and fractures in ageing and aged population. ProFaNE (Prevention of Falls Network Europe) meeting; 2004 June 11‐13; Manchester (UK). 2004.
-
- NCT00247546. Prevention of falls and injurious falls among elderly people. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00247546 (accessed 14 September 2011).
-
- Salminen M, Vahlberg T, Kivela SL. The long‐term effect of a multifactorial fall prevention programme on the incidence of falls requiring medical treatment. Public Health 2009;123(12):809‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Salminen M, Vahlberg T, Sihvonen S, Piirtola M, Isoaho R, Aarnio P, et al. Effects of risk‐based multifactorial fall prevention program on maximal isometric muscle strength in community‐dwelling aged: a randomized controlled trial. Aging‐Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;20(5):487‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Salminen M, Vahlberg T, Sihvonen S, Sjosten N, Piirtola M, Isoaho R, et al. Effects of risk‐based multifactorial fall prevention on postural balance in the community‐dwelling aged: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2009;48(1):22‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shaw 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dawson P, Chapman KL, Shaw FE, Kenny RA. Measuring the outcome of physiotherapy in cognitively impaired elderly patients who fall. Physiotherapy 1997;83(7):352.
-
- N0461021713. Physiotherapy intervention for cognitively impaired elderly fallers attending casualty. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 30 November 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0461021713]
-
- N0461044514. Risk modification of falls in cognitively impaired elderly patients attending a casualty department. A randomised controlled explanatory study. National Research Register (NRR) Archive. www.nihr.ac.uk/Pages/NRRArchiveSearch.aspx (accessed 30 November 2011). [NRR Publication ID: N0461044514]
-
- Shaw FE, Richardson DA, Dawson P, Steen IN, McKeith IG, Bond J, et al. Can multidisciplinary intervention prevent falls in patients with cognitive impairment and dementia attending a casualty department. Age and Ageing 2000;29(Suppl 1):47.
Sherrington 2014 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12607000563460. Minimising disability and falls in older people through a post‐hospital individualised exercise program. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=82384 (accessed 2 September 2011).
-
- Sherrington C, Lord SR, Vogler CM, Close JC, Howard K, Dean CM, et al. Minimising disability and falls in older people through a post‐hospital exercise program: a protocol for a randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation. BMC Geriatrics. England: Musculoskeletal Division, The George Institute for International Health, The University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia. csherrington@george.org.au, 2009; Vol. 9:8. [MEDLINE: ] - PMC - PubMed
Shumway‐Cook 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shumway‐Cook A, Silver I, Mary L, York S, Cummings P, Koepsell T. The effectiveness of a community‐based multifactorial intervention on falls and fall risk factors in community living older adults: a randomized, controlled trial. CSM 2007. Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy 2006;29(3):117. - PubMed
-
- Shumway‐Cook A, Silver IF, LeMier M, York S, Cummings P, Koepsell TD. Effectiveness of a community‐based multifactorial intervention on falls and fall risk factors in community‐living older adults: a randomized, controlled trial. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 2007; Vol. 62, issue 12:1420‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Snooks 2010 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN10538608. SAFER (Support and Assessment for Fall Emergency Referrals) Trial: Evaluation of the costs and benefits of computerised on‐scene decision support for emergency ambulance personnel to assess and plan appropriate care for older people who have fallen: a randomised controlled trial. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN10538608 (accessed 2 September 2011).
-
- Snooks H, Cheung WY, Close J, Dale J, Gaze S, Humphreys I, et al. Support and Assessment for Fall Emergency Referrals (SAFER 1) trial protocol. Computerised on‐scene decision support for emergency ambulance staff to assess and plan care for older people who have fallen: evaluation of costs and benefits using a pragmatic cluster randomised trial. BMC Emergency Medicine 2010;10:2. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomas G, Sanchez A, Snooks H. Before the fall: A discussion paper on the organisational difficulties of setting up complex randomised control trials in emergency pre‐hospital care. Emergency Medicine Journal 2011;28(3):2.
Snooks 2017 {published data only}
-
- Care of older people who fall: evaluation of the clinical and cost effectiveness of new protocols for emergency ambulance personnel to assess and refer to appropriate community based care. www.hta.ac.uk/1802 (accessed 2 May 2011).
-
- Gaze S. SAFER 2: Support and assessment for fall emergency referrals (part of the SAFER research programme. Emergency Medicine Journal 2011;28(3):3.
-
- ISRCTN60481756. Care of older people who fall: evaluation of the clinical and cost effectiveness of new protocols for emergency ambulance personnel to assess and refer to appropriate community based care ‐ a cluster randomised controlled trial. www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN60481756 (accessed 2 May 2011).
-
- Snooks HA, Anthony R, Chatters R, Dale J, Fothergill R, Gaze S, et al. Support and Assessment for Fall Emergency Referrals (SAFER) 2: a cluster randomised trial and systematic review of clinical effectiveness and cost‐effectiveness of new protocols for emergency ambulance paramedics to assess older people following a fall with referral to community‐based care when appropriate. Health Technology Assessment 2017;21(13):1‐218. [PUBMED: 28397649] - PMC - PubMed
Spink 2011 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12608000065392. Podiatry treatment to improve balance and prevent falls in older people. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=82558 (accessed 30 November 2011).
Steinberg 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Peel N. Personal communication. 10 October 2007.
-
- Peel N, Cartwright C, Steinberg M. Monitoring slips, trips and falls in the older community: preliminary results. Health Promotion Journal of Australia 1998;8(2):148‐50.
-
- Peel N, Steinberg M, Williams G. Home safety assessment in the prevention of falls among older people. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health 2000;24(5):536‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Suman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Suman S, Myint PK, Clark A, Das P, Ring L, Trepte NJ. Community‐based fall assessment compared with hospital‐based assessment in community‐dwelling older people over 65 at high risk of falling: a randomized study. Aging‐Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;23(1):35‐41. - PubMed
Swanenburg 2007 {published data only}
-
- Swanenburg J, Bruin ED, Stauffacher M, Mulder T, Uebelhart D. Effects of exercise and nutrition on postural balance and risk of falling in elderly people with decreased bone mineral density: randomized controlled trial pilot study. Clinical Rehabilitation 2007;21(6):523‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tiedemann 2015 {published data only}
-
- Tiedemann A, Paul S, Ramsay E, O'Rourke SD, Chamberlain K, Kirkham C, et al. What is the effect of a combined physical activity and fall prevention intervention enhanced with health coaching and pedometers on older adults' physical activity levels and mobility‐related goals? Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2015;15:477. [PUBMED: 25956926] - PMC - PubMed
Von Stengel 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kemmler W, Stengel S, Mayer S, Niedermayer M, Hentschke C, Kalender WA. Effect of whole body vibration on the neuromuscular performance of females 65 years and older. One‐year results of the controlled randomized ELVIS study [Effekte von ganzkorpervibrationen auf die neuromuskulare leistungsfahigkeit von frauen uber dem 65. Lebensjahr. Einjahresergebnisse der kontrollierten randomisierten ELVIS‐Studie]. Zeitschrift fur Gerontologie und Geriatrie 2010;43(2):125‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- NCT00292916. Effect of whole body vibration on bone and fall related parameters. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00292916 (accessed 31 August 2011).
-
- Stengel S, Kemmler W, Engelke K, Bebenek M, Mayhew JL, Kalender WA. Effects of whole body vibration training on the fracture risk of postmenopausal women: preliminary results of the Erlangen Longitudinal Vibration Study (ELVIS). Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2008;40(5 Suppl 1):S313.
-
- Stengel S, Kemmler W, Engelke K, Kalender WA. Effect of whole‐body vibration on neuromuscular performance and body composition for females 65 years and older: a randomized‐controlled trial. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports 2012;22(1):119‐27. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Stengel S, Kemmler W, Engelke K, Kalender WA. Effects of whole body vibration on bone mineral density and falls: results of the randomized controlled ELVIS study with postmenopausal women. Osteoporosis International 2011;22(1):317‐25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wyman 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Findorff MJ, Stock HH, Gross CR, Wyman JF. Does the Transtheoretical Model (TTM) explain exercise behavior in a community‐based sample of older women?. Journal of Aging and Health 2007;19(6):985‐1003. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Findorff MJ, Wyman JF, Nyman JA, Croghan CF. Measuring the direct healthcare costs of a fall injury event. Nursing Research 2007;56(4):283‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Lindquist R, Wyman JF, Talley KM, Findorff M, Gross CR. Design of control‐group conditions in clinical trials of behavioral interventions. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2007;39(3):214‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Nachreiner NM, Findorff MJ, Wyman JF, McCarthy TC. Circumstances and consequences of falls in community‐dwelling older women. Journal of Women's Health 2007;16(10):1437‐46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Wyman J. A home‐based fall prevention intervention for high risk older women. www.dhs.state.mn.us/main/groups/aging/documents/pub/dhs16_137823.pdf (accessed 14/10/07).
Xia 2009 {published data only}
Yamada 2013 {published data only}
-
- Yamada M, Higuchi T, Nishiguchi S, Yoshimura K, Kajiwara Y, Aoyama T. Multitarget stepping program in combination with a standardized multicomponent exercise program can prevent falls in community‐dwelling older adults: a randomized, controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2013;61(10):1669‐75. [PUBMED: 24001116] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12607000206426 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12607000206426. Community care and hospital based collaborative falls prevention project. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=81955 (accessed 12 June 2017).
ACTRN12614000827639 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12614000827639. Does nutrition and exercise prevent frailty and reduce falls in pre‐frail older adults in New Zealand?. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=366773 (accessed 12 June 2017).
ACTRN12615001326583 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12615001326583. Preventing falls in older people after discharge from hospital as a result of a fall. anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=369603 (accessed 12 June 2017).
Barker 2015 {published data only}
-
- Barker AL, Cameron PA, Hill KD, Flicker L, Haines TP, Lowthian JA, et al. RESPOND‐‐A patient‐centred programme to prevent secondary falls in older people presenting to the emergency department with a fall: protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Injury prevention : Journal of the International Society for Child and Adolescent Injury Prevention 2015;21(1):e1. [PUBMED: 24958769] - PubMed
-
- Morello RT, Morris RL, Hill KD, Haines TP, Arendts G, Redfern J, et al. RESPOND: a programme to prevent secondary falls in older people presenting to the emergency department with a fall: protocol for an economic evaluation. Injury prevention : journal of the International Society for Child and Adolescent Injury Prevention 2017;23(2):124‐30. [PUBMED: 28330932] - PubMed
Blank 2011 {published data only}
-
- NCT01032252. Prevention of falls in general practitioner for community‐dwelling older adults [PreFalls]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01032252 (accessed August 2011).
Close 2014 {published data only}
-
- Close JC, Wesson J, Sherrington C, Hill KD, Kurrle S, Lord SR, et al. Can a tailored exercise and home hazard reduction program reduce the rate of falls in community dwelling older people with cognitive impairment: protocol paper for the i‐FOCIS randomised controlled trial. BMC geriatrics 2014;14:89. [PUBMED: 25128411] - PMC - PubMed
Hill 2017 {published data only}
-
- Hill AM, Etherton‐Beer C, McPhail SM, Morris ME, Flicker L, Shorr R, et al. Reducing falls after hospital discharge: a protocol for a randomised controlled trial evaluating an individualised multimodal falls education programme for older adults. BMJ Open 2017;7(2):e013931. [PUBMED: 28153933] - PMC - PubMed
ISRCTN21120199 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN21120199. The effect of an assessment‐based falls prevention programme in elderly people utilising day‐care services. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN21120199 (accessed 13 June 2017).
Landi 2017 {published data only}
-
- Landi F, Cesari M, Calvani R, Cherubini A, Bari M, Bejuit R, et al. The "Sarcopenia and Physical fRailty IN older people: multi‐componenT Treatment strategies" (SPRINTT) randomized controlled trial: design and methods. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research 2017;29(1):89‐100. [PUBMED: 28144914] - PubMed
NCT01080196 {published data only}
-
- NCT01080196. Reducing falls with RENEW in older adults who have fallen. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01080196 (accessed 31 August 2011).
NCT01552551 {published data only}
-
- NCT01552551. Assessment and referral versus exercise in primary prevention of falls: PA Healthy Steps Program. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT01552551 (accessed 13 June 2017).
NCT01713543 {published data only}
-
- NCT01713543. Community‐based falls prevention program for the elderly. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01713543 (accessed 12 June 2017).
NCT02374307 {published data only}
-
- NCT02374307. Falls‐prevention in older people receiving home‐help services. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02374307 (accessed 12 June 2017).
NCT02631330 {published data only}
-
- NCT02631330. Effect on falls reduction of a multimodal intervention in frail and pre‐frail elderly community‐dwelling people (FAREMAVA). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02631330 (accessed 12 June 2017).
Sherrington 2016 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12610000805077. RESTORE: Recovery exercises and Stepping On after fracture. www.anzctr.org.au/trial_view.aspx?ID=335781 (accessed 12 June 2017).
-
- Sherrington C, Fairhall N, Kirkham C, Clemson L, Howard K, Vogler C, et al. Exercise and fall prevention self‐management to reduce mobility‐related disability and falls after fall‐related lower limb fracture in older people: protocol for the RESTORE (Recovery Exercises and STepping On afteR fracturE) randomised controlled trial. BMC Geriatrics 2016;16:34. [PUBMED: 26838998] - PMC - PubMed
Tan 2014 {published data only}
Additional references
ACSQH 2009
-
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Healthcare. Preventing falls and harm from falls in older people. Best Practice Guidelines for Australian Community Care 2009. www.safetyandquality.gov.au/wp‐content/uploads/2012/01/Guidelines‐COMM.pdf (accessed 27 May 2016).
American Geriatrics Society 2011
-
- Panel on Prevention of Falls in Older Persons, American Geriatrics Society and British Geriatrics Society. Summary of the updated American Geriatrics Society/British Geriatrics Society clinical practice guideline for prevention of falls in older persons. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2011;59(1):148‐57. [PUBMED: 21226685] - PubMed
Berry 2008
Bhasin 2018
-
- Bhasin S, Gill TM, Reuben DB, Latham NK, Gurwitz JH, Dykes P, et al. Strategies to reduce injuries and develop confidence in elders (STRIDE): a cluster‐randomized pragmatic trial of a multifactorial fall injury prevention strategy: design and methods. Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 2018;73(8):1053‐61. [DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glx190; PUBMED: 29045582] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Burns 2016
Cameron 2012
Campbell 1990
-
- Campbell AJ, Borrie MJ, Spears GF, Jackson SL, Brown JS, Fitzgerald JL. Circumstances and consequences of falls experienced by a community population 70 years and over during a prospective study. Age and Ageing 1990;19(2):136‐41. [PUBMED: 2337010] - PubMed
Campbell 2006
-
- Campbell AJ, Robertson MC. Implementation of multifactorial interventions for fall and fracture prevention. Age and Ageing 2006;35 Suppl 2:ii60‐4. [PUBMED: 16926208] - PubMed
Canning 2015
Copsey 2016
Deandrea 2010
-
- Deandrea S, Lucenteforte E, Bravi F, Foschi R, Vecchia C, Negri E. Risk factors for falls in community‐dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Epidemiology 2010;21(5):658‐68. [PUBMED: 20585256] - PubMed
Gates 2008
Goodwin 2014
Hannan 2010
-
- Hannan MT, Gagnon MM, Aneja J, Jones RN, Cupples LA, Lipsitz LA, et al. Optimizing the tracking of falls in studies of older participants: comparison of quarterly telephone recall with monthly falls calendars in the MOBILIZE Boston Study. American Journal of Epidemiology 2010;171(9):1031‐6. [PUBMED: 20360242] - PMC - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16.3.4: Approximate analyses of cluster‐randomized trials for meta‐analysis: effective sample sizes. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011c
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9. Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011d
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16.5.4 How to include multiple groups from one study. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kellogg 1987
-
- Anonymous. The prevention of falls in later life. A report of the Kellogg International Work Group on the Prevention of Falls by the Elderly. Danish Medical Bulletin 1987;34 Suppl 4:1‐24. - PubMed
Kendrick 2014
Laird 2001
-
- Laird RD, Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D. Fall history is an independent predictor of adverse health outcomes and utilization in the elderly. American Journal of Managed Care 2001;7(12):1133‐8. [PUBMED: 11767299] - PubMed
Lamb 2005
-
- Lamb SE, Jørstad‐Stein EC, Hauer K, Becker C, Prevention of Falls Network Europe and Outcomes Consensus Group. Development of a common outcome data set for fall injury prevention trials: the Prevention of Falls Network Europe consensus. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2005;53(9):1618‐22. [PUBMED: 16137297] - PubMed
Lamb 2007
-
- Lamb SE, Hauer K, Becker C. Manual for the fall prevention classification system. Version 1 (4 April 2007). www.profane.eu.org/documents/Falls_Taxonomy.pdf (accessed 17 May 2016).
Lamb 2011
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6.4.11.1 The Cochrane Highly Sensitive Search Strategies for identifying randomized trials in MEDLINE. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
NICE 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Falls in older people: assessing risk and prevention 2013 [CG161]. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg161/chapter/1‐recommendations (accessed 27 May 2016). - PubMed
Peel 2002
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rizzo 1996
-
- Rizzo JA, Baker DI, McAvay G, Tinetti ME. The cost‐effectiveness of a multifactorial targeted prevention program for falls among community elderly persons. Medical Care 1996;34(9):954‐69. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sach 2012
-
- Sach TH, Logan PA, Coupland CA, Gladman JR, Sahota O, Stoner‐Hobbs V, et al. Community falls prevention for people who call an emergency ambulance after a fall: an economic evaluation alongside a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2012; Vol. 41, issue 5:635‐41. [DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afs071] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Scuffham 2003
Sherrington 2016a
Sherrington 2016b
-
- Sherrington C, Michaleff ZA, Fairhall N, Paul SS, Tiedemann A, Whitney J, et al. Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: an updated systematic review and meta‐analysis. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2016;51(24):1750‐8. [PUBMED: 27707740] - PubMed
Smeeth 2002
-
- Smeeth L, Ng ES. Intraclass correlation coefficients for cluster randomized trials in primary care: data from the MRC Trial of the Assessment and Management of Older People in the Community. Controlled Clinical Trials 2002;23(4):409‐21. - PubMed
Stata 2015
-
- StataCorp. 2015. Stata Statistical Software: Release 14. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP.
Tinetti 1988
-
- Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. New England Journal of Medicine 1988;319(26):1701‐7. [PUBMED: 3205267] - PubMed
Tinetti 1997
-
- Tinetti ME, Williams CS. Falls, injuries due to falls, and the risk of admission to a nursing home. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(18):1279‐84. [PUBMED: 9345078] - PubMed
Tinetti 2003
-
- Tinetti ME. Clinical practice. Preventing falls in elderly persons. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348(1):42‐9. [PUBMED: 12510042] - PubMed
Todd 2004
-
- Todd C, Skelton D. What are the main risk factors for falls among older people and what are the most effective interventions to prevent these falls? March 2004. Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe (Health Evidence Network report). www.euro.who.int/document/E82552.pdf (accessed 28 April 2016).
Tricco 2017
Verheyden 2013
Vieira 2016
-
- Vieira ER, Palmer RC, Chaves PH. Prevention of falls in older people living in the community. BMJ 2016;353:i1419. - PubMed
Walters 2003
Yardley 2002
-
- Yardley L, Smith H. A prospective study of the relationship between feared consequences of falling and avoidance of activity in community‐living older people. Gerontologist 2002;42(1):17‐23. [PUBMED: 11815695] - PubMed
Zecevic 2006
-
- Zecevic AA, Salmoni AW, Speechley M, Vandervoort AA. Defining a fall and reasons for falling: comparisons among the views of seniors, health care providers, and the research literature. Gerontologist 2006;46(3):367‐76. [PUBMED: 16731875] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Gillespie 2012
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

