Vitamin B₆ and Its Role in Cell Metabolism and Physiology
- PMID: 30037155
- PMCID: PMC6071262
- DOI: 10.3390/cells7070084
Vitamin B₆ and Its Role in Cell Metabolism and Physiology
Abstract
Vitamin B₆ is one of the most central molecules in cells of living organisms. It is a critical co-factor for a diverse range of biochemical reactions that regulate basic cellular metabolism, which impact overall physiology. In the last several years, major progress has been accomplished on various aspects of vitamin B₆ biology. Consequently, this review goes beyond the classical role of vitamin B₆ as a cofactor to highlight new structural and regulatory information that further defines how the vitamin is synthesized and controlled in the cell. We also discuss broader applications of the vitamin related to human health, pathogen resistance, and abiotic stress tolerance. Overall, the information assembled shall provide helpful insight on top of what is currently known about the vitamin, along with addressing currently open questions in the field to highlight possible approaches vitamin B₆ research may take in the future.
Keywords: PLP; cell; health; metabolism; pathogen; physiology; pyridoxine; stress; vitamin B6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


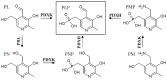

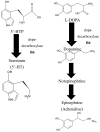

References
-
- Choudhury S.R., Singh S.K., Roy S., Sengupta D.N. An insight into the sequential, structural and phylogenetic properties of banana 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase 1 and study of its interaction with pyridoxal-5′-phosphate and aminoethoxyvinylglycine. J. Biosci. 2010;35:281–294. doi: 10.1007/s12038-010-0032-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

