Lead fracture of peripheral nerve stimulator for brachial plexopathy -a case report
- PMID: 30037173
- PMCID: PMC6193596
- DOI: 10.4097/kja.d.17.00023
Lead fracture of peripheral nerve stimulator for brachial plexopathy -a case report
Abstract
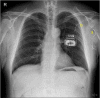
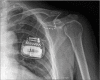
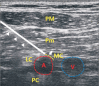
Peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) is a useful treatment for chronic pain, but it can cause damage depending on its application site. Here, we describe the case of a 54-year-old man who underwent PNS for brachial plexopathy in 2015. One lead was implanted on the left medial cord to stimulate the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve, and the other was implanted on the radial nerve to stimulate the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve. Both leads were inserted near the shoulder joint but did not cross it. Before PNS, the patient did not move his shoulder and elbow because of severe pain, but the treatment greatly alleviated this pain. Twenty months after the operation, both leads were fractured, and the severe pain returned. Repetitive motion near the joint was closely related to the lead fractures. In conclusion, large joints as the insertion sites of PNS leads should be avoided to prevent lead fractures.
Keywords: Complications; Fracture; Lead; Peripheral nerve; Stimulation..
Figures
References
-
- Deer TR, Mekhail N, Provenzano D, Pope J, Krames E, Leong M, et al. The appropriate use of neurostimulation of the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system for the treatment of chronic pain and ischemic diseases: the Neuromodulation Appropriateness Consensus Committee. Neuromodulation. 2014;17:515–50. - PubMed
-
- Park CH, Huh BK. Permanent peripheral nerve stimulation for chronic occipital neuralgia: case reports. Korean J Pain. 2008;21:155–8.
-
- Chung W, Kim Y, Lee J, Lee S, Kim Y, Shin Y, et al. Ultrasound-guided placement of a permanent peripheral nerve stimulator in a patient with complex regional pain syndrome: A case report. Anesth Pain Med. 2016;11:295–8.
-
- Eldabe S, Buchser E, Duarte RV. Complications of spinal cord stimulation and peripheral nerve stimulation techniques: a review of the literature. Pain Med. 2016;17:325–36. - PubMed
-
- Sharan A, Huh B, Narouze S, Trentman T, Mogilner A, Vaisman J, et al. Analysis of adverse events in the management of chronic migraine by peripheral nerve stimulation. Neuromodulation. 2015;18:305–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

