Effect of local infiltration analgesia, peripheral nerve blocks, general and spinal anesthesia on early functional recovery and pain control in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 30037342
- PMCID: PMC6056928
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-018-2165-9
Effect of local infiltration analgesia, peripheral nerve blocks, general and spinal anesthesia on early functional recovery and pain control in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: The aim of the study was to analyze the effect of local infiltration analgesia (LIA), peripheral nerve blocks, general and spinal anesthesia on early functional recovery and pain control in primary unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA).
Methods: Between January 2016 until August 2016, 134 patients underwent primary UKA and were subdivided into four groups according to their concomitant pain and anesthetic procedure with catheter-based techniques of femoral and sciatic nerve block (group GA&FNB, n = 38) or epidural catheter (group SP&EPI, n = 20) in combination with general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia, respectively, and LIA combined with general anesthesia (group GA&LIA, n = 46) or spinal anesthesia (group SP&LIA, n = 30). Outcome parameters focused on the evaluation of pain (NRS scores), mobilization, muscle strength and range of motion up to 7 days postoperatively. The cumulative consumption of (rescue) pain medication was analyzed.
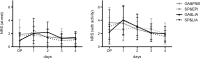
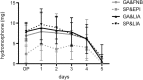
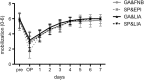
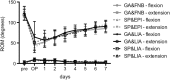
Results: The LIA groups revealed significantly lower (about 50%) mean NRS scores (at rest) compared to the catheter-based groups at the day of surgery. In the early postoperative period, the dose of hydromorphone as rescue pain medication was significantly lower (up to 68%) in patients with SP&EPI compared to all other groups. No significant differences could be detected with regard to grade of mobilization, muscle strength and range of motion. However, there seemed to be a trend towards improved mobilization and muscle strength with general anesthesia and LIA, whereof general anesthesia generally tended to ameliorate mobilization.
Conclusions: Except for a significant lower NRS score at rest in the LIA groups at day of surgery, pain relief was comparable in all groups without clinically relevant differences, while the use of opioids was significantly lower in patients with SP&EPI. A clear clinically relevant benefit for LIA in UKA cannot be stated. However, LIA offers a safe and effective treatment option comparable to the well-established conventional procedures.
Keywords: Epidural catheter; Femoral nerve block; General anesthesia; Local infiltration analgesia; Spinal anesthesia; Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study adhered to the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. It was conducted according to ICMJE guidelines. Written consent was obtained from all participants for the surgical and anesthetic procedures; further consent for retrospective analysis of the data was waived by the Ethics Committee of the Bavarian State Chamber of Physicians (ID: 2017–109).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

