Affordability of essential medicine prices in Malaysia's private health sector
- PMID: 30038489
- PMCID: PMC6052935
- DOI: 10.2147/PPA.S151603
Affordability of essential medicine prices in Malaysia's private health sector
Abstract
Background: The lack of price control in Malaysia has led to increased market competition, resulting in high medicine prices, notably in the private sector. This largely affects patients' out-of-pocket expenses in the private sector. Although generic medicines are preferred due to affordability, the prices are still notably high.
Methods: This study compares innovator and generic medicine prices to estimate treatment affordability in the private sector. Private hospitals and community retail pharmacies were examined from 2011 to 2015. Data were collected on the basis of recommendations by the World Health Organization's Health Action International.
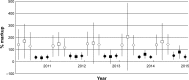
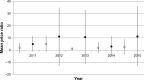
Results: The markup of generic medicines was significantly higher than that of innovator medicines during the study period (p<0.001). While the markup of generic medicine was 31%-402% (36%-171% and 31%-402% for core and supplementary list items), that of innovator medicine was 24%-86% (28%-86% and 24%-80% for core and supplementary list items). There was no significant increase in the median price ratio for 11 selected generic medicines (from 1.8±3.9 to 2.9±8.2) (p>0.05). However, the median price ratio of the 11 innovator medicines significantly increased (from 4.9±6.1 to 11.2±20.3) (p=0.045). Affordability of all generic medicines was below the 2-day wage for treatment, with captopril (25 mg tablet) reporting the highest cost (1.1-1.7-day wages). Among innovator medicines, omeprazole (20 mg capsule; 6.2-7.0 days' wages) reported the highest median treatment cost.
Conclusion: There is a need for policies to control national drug prices, to ensure medicine prices are monitored. This can help keep out-of-pocket expenses, especially in middle-income countries such as Malaysia, at a minimal in the private sector.
Keywords: community medicine; hospital; patient education; pharmacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Cameron A, Ewen M, Ross-Degnan D, Ball D, Laing R. Medicine prices, availability, and affordability in 36 developing and middle-income countries: a secondary analysis. Lancet. 2009;373(9659):240–249. - PubMed
-
- Safurah J, Kamaliah MN, Khairiyah AM, Nour O, Healy J. Malaysia health system review. Health Syst Transit. 2013;3(1):44.
-
- Baber ZUD, Ibrahim MIM. Affordability of medicines in Malaysia – consumer perceptions. Essent Drugs Monit. 2003;33:18–19.
-
- Hassali MA, Shafie AA, Babar ZUD, Khan TM. A study comparing the retail drug prices between Northern Malaysia and Australia. J Pharm Health Serv Res. 2012;3:103–107.
-
- Hassali MA, Siang TC, Yen ZW, Saleem F, Alrasheedy AA. Pharmaceutical pricing in Malaysia. In: Babar ZUD, editor. Pharmaceutical Prices in the 21st Century. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2014. pp. 171–188.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

