High prevalence and indexes of anti-John Cunningham virus antibodies in a cohort of Chinese patients with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 30038791
- PMCID: PMC6050819
- DOI: 10.1177/2055217318788699
High prevalence and indexes of anti-John Cunningham virus antibodies in a cohort of Chinese patients with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
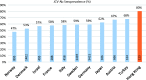
We performed a cross-sectional study in 123 Chinese multiple sclerosis patients residing in Hong Kong to evaluate their anti-John Cunningham virus status using STRATIFY JCV DxSelect assays. Anti-John Cunningham virus antibody was present in 98/123 (80%) subjects, among which 75/98 (77%) had an anti-John Cunningham virus index ≥1.5. Anti-John Cunningham virus antibody seropositivity was not correlated with age, disease duration, Expanded Disability Status Scale scores, types of multiple sclerosis (relapsing vs progressive), or disease-modifying treatments used. We found a very high seroprevalence and index of anti-John Cunningham virus antibodies in Chinese multiple sclerosis patients, which may impact the risk assessment and recommendation of disease-modifying treatments in this population.
Keywords: Anti-John Cunningham virus antibody; Chinese; anti-John Cunningham virus index; multiple sclerosis; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
Figures

References
-
- Lau A, Au CCK, Wong A.et al. Clinical features and updated epidemiology data of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica from the Hong Kong Multiple Sclerosis Registry. Mult Scler J 2015; 21: 108–109.
-
- Wattjes MP, Warnke C. Guidelines on PML risk stratification and diagnosis in patients with MS treated with natalizumab: So far so good? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2016; 87: 115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

