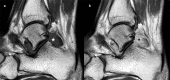
Diffuse Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis of the Subtalar Joint
- PMID: 30039025
- PMCID: PMC6032406
- DOI: 10.5334/jbsr.1477
Diffuse Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis of the Subtalar Joint
Keywords: MRI; PVNS; ankle; diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

