Interferon gamma in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 30039553
- PMCID: PMC6143921
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1700
Interferon gamma in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
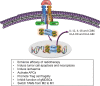
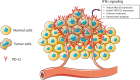
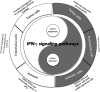
Immune system can recognize self vs transformed self. That is why cancer immunotherapy achieves notable benefits in a wide variety of cancers. Recently, several papers reported that immune checkpoint blockade therapy led to upregulation of IFNγ and in turn clearance of tumor cells. In this review, we conducted an extensive literature search of recent 5-year studies about the roles of IFNγ signaling in both tumor immune surveillance and immune evasion. In addition to well-known functions, IFNγ signaling also induces tumor ischemia and homeostasis program, resulting in tumor clearance and tumor escape, respectively. The yin and the yang of IFNγ signaling are summarized. Thus, this review helps us to comprehensively understand the roles of IFNγ in tumor immunity, which contributes to better design and management of clinical immunotherapy approaches.
Keywords: IFNγ signaling; cancer immunotherapy; immune evasion; immune surveillance; transformed self.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Tian T, Olson S, Whitacre JM, Harding A. The origins of cancer robustness and evolvability. Integr Biol (Camb). 2011;3:17‐30. - PubMed
-
- Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD. Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:836‐848. - PubMed
-
- Dulos J, Carven GJ, van Boxtel SJ, et al. PD‐1 blockade augments Th1 and Th17 and suppresses Th2 responses in peripheral blood from patients with prostate and advanced melanoma cancer. J Immunother. 2012;35:169‐178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

