Genes regulated by SATB2 during neurodevelopment contribute to schizophrenia and educational attainment
- PMID: 30040823
- PMCID: PMC6097700
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007515
Genes regulated by SATB2 during neurodevelopment contribute to schizophrenia and educational attainment
Abstract
SATB2 is associated with schizophrenia and is an important transcription factor regulating neocortical organization and circuitry. Rare mutations in SATB2 cause a syndrome that includes developmental delay, and mouse studies identify an important role for SATB2 in learning and memory. Interacting partners BCL11B and GATAD2A are also schizophrenia risk genes indicating that other genes interacting with or are regulated by SATB2 are making a contribution to schizophrenia and cognition. We used data from Satb2 mouse models to generate three gene-sets that contain genes either functionally related to SATB2 or targeted by SATB2 at different stages of development. Each was tested for enrichment using the largest available genome-wide association studies (GWAS) datasets for schizophrenia and educational attainment (EA) and enrichment analysis was also performed for schizophrenia and other neurodevelopmental disorders using data from rare variant sequencing studies. These SATB2 gene-sets were enriched for genes containing common variants associated with schizophrenia and EA, and were enriched for genes containing rare variants reported in studies of schizophrenia, autism and intellectual disability. In the developing cortex, genes targeted by SATB2 based on ChIP-seq data, and functionally affected when SATB2 is not expressed based on differential expression analysis using RNA-seq data, show strong enrichment for genes associated with EA. For genes expressed in the hippocampus or at the synapse, those targeted by SATB2 are more strongly enriched for genes associated EA than gene-sets not targeted by SATB2. This study demonstrates that single gene findings from GWAS can provide important insights to pathobiological processes. In this case we find evidence that genes influenced by SATB2 and involved in synaptic transmission, axon guidance and formation of the corpus callosum are contributing to schizophrenia and cognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



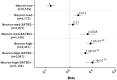

References
-
- Srinivasan K, Leone DP, Bateson RK, Dobreva G, Kohwi Y, et al. (2012) A network of genetic repression and derepression specifies projection fates in the developing neocortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109: 19071–19078. 10.1073/pnas.1216793109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Britanova O, Akopov S, Lukyanov S, Gruss P, Tarabykin V (2005) Novel transcription factor Satb2 interacts with matrix attachment region DNA elements in a tissue-specific manner and demonstrates cell-type-dependent expression in the developing mouse CNS. Eur J Neurosci 21: 658–668. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03897.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

